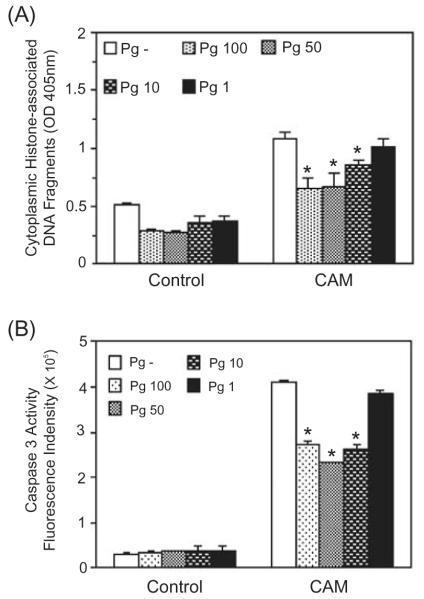
Fig. 1.
Porphyromonas gingivalis infection protects gingival epithelial cells against camptothecin-induced apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner. Primary GECs were infected with P. gingivalis 33277 for 20 h at moi of 1, 10, 50 and 100 or were mock-infected (Pg-). Camptothecin (CAM) at 1 μgml−1 was added to the cells for an additional 4 h. Control represents GEC without CAM treatment.
A. ELISA for histone-associated DNA fragments in the cytoplasm.
B. Caspase-3 activity assessed by cleavage of the fluorescent substrate Ac-DEVD-AMC (arbitrary units).
Error bars represent SD, n = 3. An asterisk denotes statistical difference of P. gingivalis-infected from mock-infected, P < 0.01, t-test.