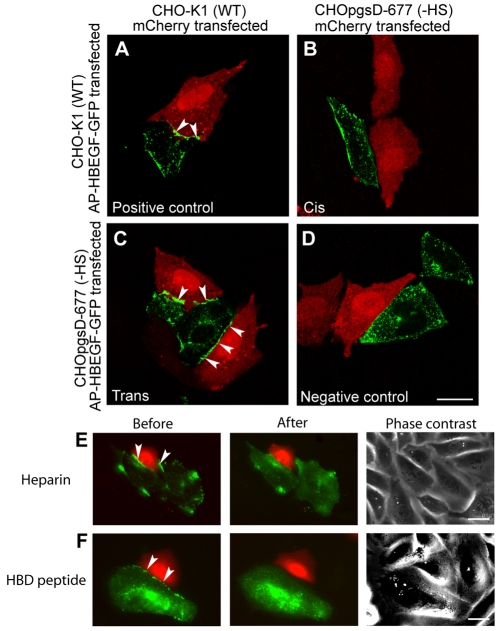
Fig. 6.
HSPGs interact in trans with pro-HB-EGF. Confocal imaging of the localization of HB-EGF (green) at the junction of an mCherry (red)-transfected cell and an AP–HB-EGF–GFP-transfected cell. (A) Positive control sample with AP–HB-EGF–GFP and mCherry both in CHO-K1 (wild-type) cells had HB-EGF at sites of cell-cell contact (arrowheads). (B) Cis binding with AP–HB-EGF–GFP in CHO-K1 (wild-type) cells and mCherry in CHO-pgsD677 cells [– heparan sulfate (HS)] showed little HB-EGF at sites of cell-cell contact. (C) Trans binding with AP–HB-EGF–GFP in CHOpgsD-677 (–HS) cells and mCherry in CHO-K1 (wild-type) cells showed HB-EGF present at the cell-cell junction (arrowheads). (D) Negative control sample with AP–HB-EGF–GFP and mCherry in CHOpgsD-677 (–HS) cells showed no concentration of HB-EGF at the cell-cell junction. Trans binding epifluorescence sample images were taken before and after treatment with (E) heparin (100 μg/ml) for 15 minutes or (F) an HBD peptide (100 μM) for 2 hours, which dissociated the ligand from sites of cell-cell contact between an AP–HB-EGF–GFP transfected CHOpgsD-677 (–HS) cell and an mCherry-transfected CHO-K1 (wild-type) cell. Each experiment was repeated three or more times. Scale bars: 20 μm.