Fig. 3.
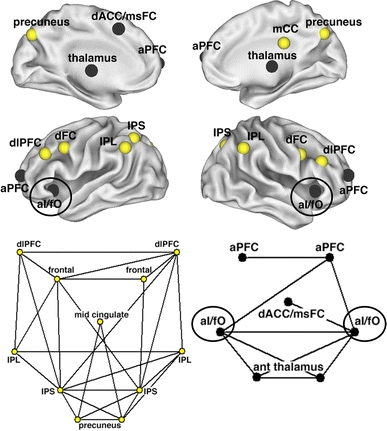
The anterior insula (aI) forms part of a cingulo-opercular control network, distinct from a fronto-parietal control network. Human cingulo-opercular (black) and fronto-parietal (yellow) control networks displayed on inflated brain surfaces. The network structure of human control networks is displayed as a two-dimensional pseudo-anatomical graph layout. Black lines indicate strong resting state functional connections between brain regions. Adapted from Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (Dosenbach et al. 2007). Copyright (2007), with permission from National Academy of Sciences, USA
