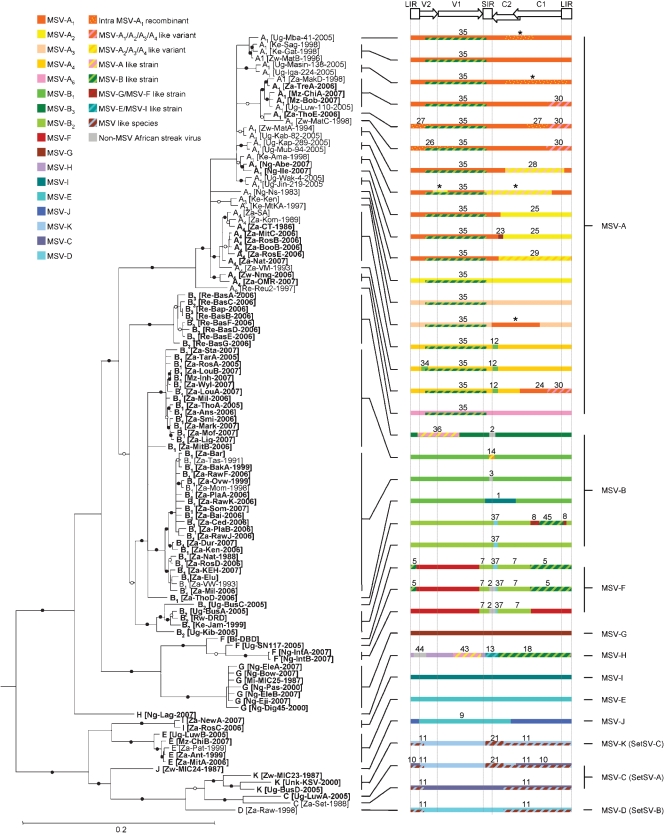
Fig. 1.
Complex relationships amongst MSV isolates sampled throughout Africa and the Indian Ocean island of La Réunion. Whereas tree branches with less than 50 % bootstrap support have been collapsed, those with greater than 70 and 90 % support are labelled with open and filled-in circles respectively. The tree was rooted using Panicum streak virus (isolate Karino; GenBank accession no. L39638) as an outgroup (not shown). Virus names take the form Strainvariant [country–region–laboratory ID–year of isolation]. Variant numbers are equivalent to the subtype designators given in other publications (Owor et al., 2007b; Martin et al., 2001). Wherever representation of older recombination events would have obscured the representation of more recent recombination events, the older events have been displayed as a thinner bar. Hatched regions indicate tracts of sequence either transferred from currently unsampled MSV strains during a relatively recent recombination event, or transferred between ancestral sequences during a more ancient recombination event. Numbers associated with recombination events correspond with those in Supplementary Table S3. Events marked with an asterisk were characterized in Owor et al. (2007b). Positions of genomic features are indicated above the coloured bars: V2, movement protein gene; V1, coat protein gene; C1/C2, replication-associated protein gene; C1, repA gene; LIR, long intergenic region; SIR, short intergenic region. Bar, 0.2 nucleotide substitutions per site.