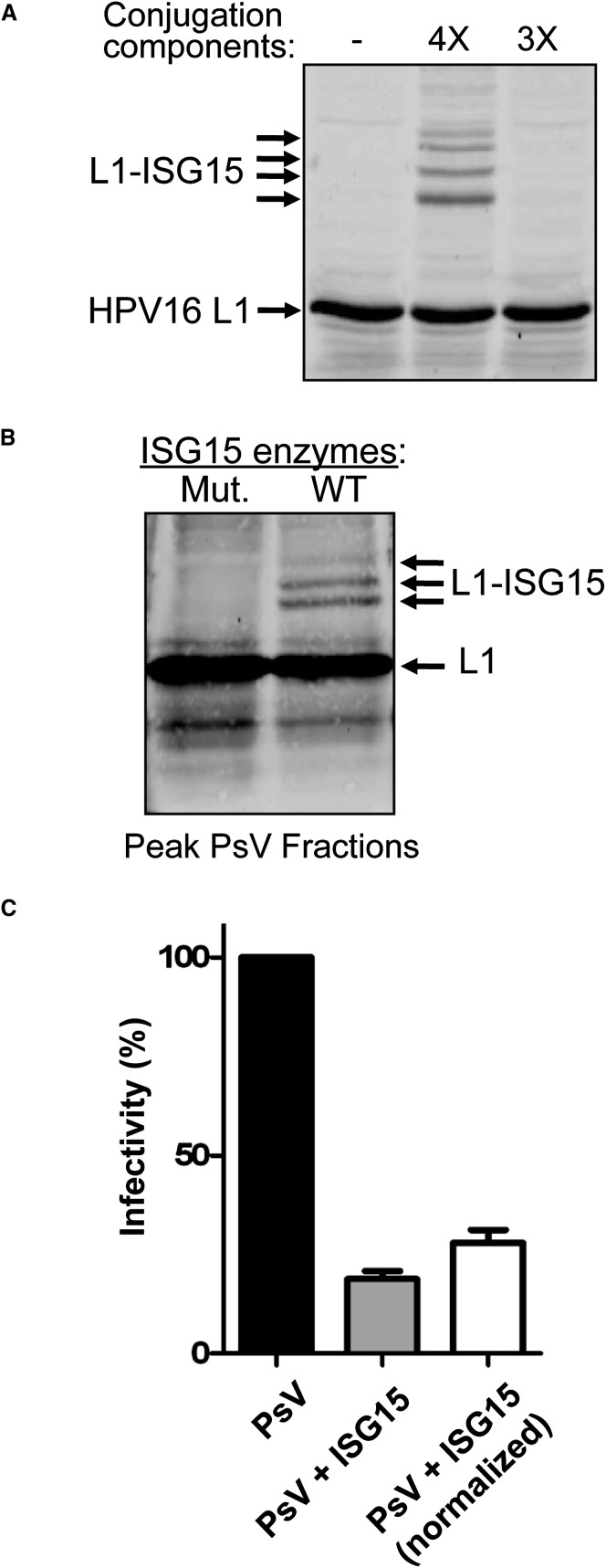
Figure 7.
ISGylation of HPV16 L1 Has a Dominant-Negative Effect on Infectivity of HPV Pseudovirus
(A) ISG15 Modification of HPV16 L1. 293TT cells were cotransfected with p16shell, alone, or with plasmids expressing ISG15, Ube1L, UbcH8, and Herc5 (4×), or this set of plasmids without ISG15 (3×). Cells extracts were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with anti-L1 antibody.
(B) ISGylated HPV16 L1 is detected in fractions containing HPV pseudovirus. Equal volumes of PsV-containing fractions, prepared in cells expressing active ISGylation enzymes (WT) or inactive mutants (Mut.), were separated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with anti-L1 antibody.
(C) ISGylation of HPV16 L1 decreases the infectivity of HPV pseudovirus. 293T cells were infected with equal volumes PsV from the fractions shown in Figure 7B, formed either in the absence (PsV) or presence (PsV + ISG15) of the ISG15 conjugation system. GFP-positive cells were counted 60 hr postinfection by FACS. The infectivity of wild-type PsV was set to 100%. Results are presented both without (middle) and with (right) normalization for total L1 protein concentration. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean of three independent experiments performed in triplicate.