Fig. 2.
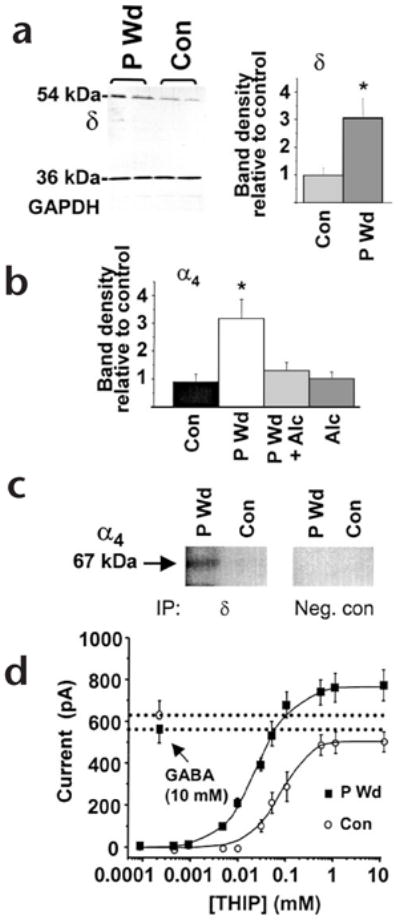
Progesterone withdrawal increases α4βδ GABAA receptors. (a) Left, western blot showing increased expression of the δ subunit (54 kDa), but not a control protein (GAPDH, 36 kDa) after progesterone withdrawal (P Wd) compared to control (Con). Right, mean values (n = 20–25, performed in triplicate). (b) Increases in α4 protein following P Wd were prevented by in vivo administration of alcohol (0.5 g/kg × 3, intraperitoneally) during the final two hours of the withdrawal period (P Wd + Alc; n = 9–10). (c) Co-assembly of α4 and δ GABAA receptor subunits. After immunoprecipitation (IP) using protein A beads coupled to antibodies for the δ subunit (IP, δ) or a cytosolic protein (IP, Neg. con) membranes were probed with digoxygenin-labeled anti-α4 on a western blot (n = 4 hippocampi, in duplicate). A prominent 67-kDa band was detected after P Wd, but was barely detectable under control conditions. (d) The maximum current produced by THIP compared to that produced by 10 mM GABA was 1.41 after P Wd (THIP EC50 = 39 ± 2 μM), and 0.95 in control neurons (THIP EC50 = 81 ± 6 μM). This was determined using whole-cell patch clamp recording in neurons from CA1 hippocampus (n = 10–15, *P < 0.05).
