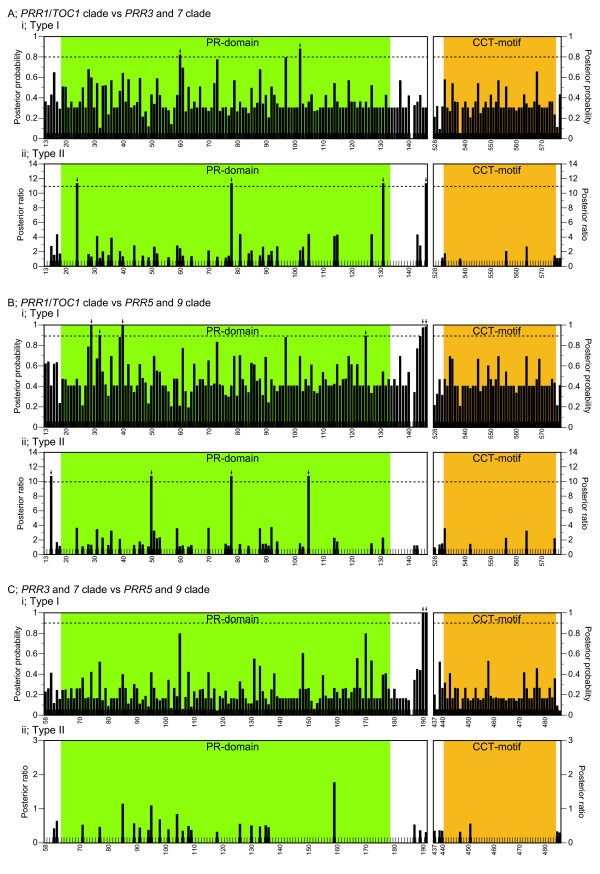
Figure 4.
Type I and type II functional divergences among the PRR gene clades. Coefficients of type I (i) and type II (ii) functional divergences between PRR1/TOC1 clade and PRR3 and 7 clade (A), between PRR1/TOC1 clade and PRR5 and 9 clade (B) and between PRR3 and 7 clade and PRR5 and 9 clade (C) were calculated by DIVERGE 2.0 [55,56] using the TCoffee alignment (see Additional file 3) and the ME tree (Figure 2). Right and left panels indicate the PR-domain and its flanking region, and the CCT-motif and its flanking region, respectively. Positions of amino acid residues correspond to AtPRR1/TOC1 in PRR1/TOC1 clade vs PRR3 and 7 clade, AtPRR1/TOC1 in PRR1/TOC1 clade vs PRR5 and 9 clade and to AtPRR3 in PRR3 and 7 clade vs PRR5 and 9 clade. Cutoff values of the posterior probability and posterior ratio were established empirically by sequentially removing the highest scoring sites from the alignment until θ = 0. The cutoff values are shown by broken lines. The value of θII between PRR3 and 7 clade and PRR5 and 9 clade was not set because the coefficient of the θII was not significantly greater than zero. Thus, there is no broken line shown in the bottom panel (C, ii). The regions represented in this figure are surrounded with blue boxes in Additional file 3. Arrows indicate sites above the empirical cutoff values. Green and yellow shadings on the panels indicate PR-domain and CCT-motif, respectively.