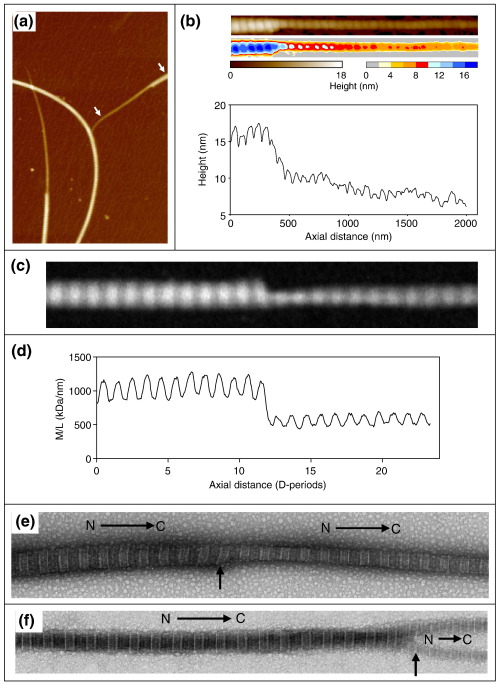
Fig. 3.
Ultrastructure over the growth junction of seed fibrils. AFM was performed on air-dried samples deposited on freshly cleaved mica using a Veeco Multimode with a Nanoscope IIIa controller operating in intermittent contact mode. (a) Typical AFM image of seed fibrils and tip projections after 2 h of growth. The specimen area is 4 μm × 6 μm and is scaled to 20 nm in height. A fibril plus tip lying between the white arrows in (a) is shown straightened (using ImageJ11) in the upper part of (b). The height scale is 18 nm and is shown displayed with continuous and discontinuous look-up tables. A height plot for a midposition along the fibril axis is shown in the lower part of (b). A dark-field STEM image of an unstained fibril seed–spur junction is shown in (c) and the derived axial mass distribution in (d). The periodic gap–overlap structure is clearly visible in both AFM and STEM and continues in phase over the junction between seed fibril and projection. (e and f) Typical TEM images of seed–spur junctions (vertical arrows) with 1 and 2 spurs, respectively, after negative staining with 2% uranyl acetate. Molecular polarity (N→C), as indicated by the stain pattern,12 is preserved across the junction as shown. D period = 67 nm.