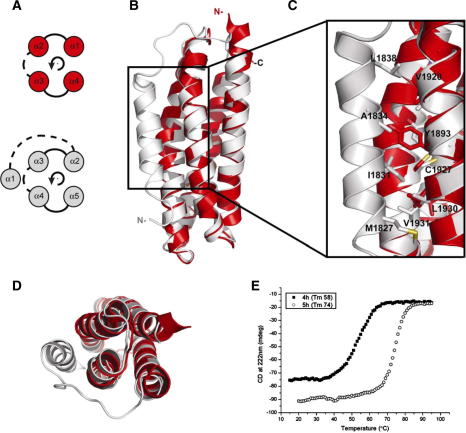
Fig. 2.
Structural comparisons between the 5-helix and the 4-helix bundles. (A) Topology diagram of the 4-helix up-and-down fold (red) and the 5-helix left-handed crossover connectivity fold (grey) common in the talin rod. Solid and dashed lines represent connecting loops on opposite ends of the helices. Helices 1–4 in the 4-helix are equivalent to helices 2–5 in the 5-helix. (B) Overlay of the structures of 1815–1973 (grey) and 1843–1973 (red) showing the similarity of the core domain and the location of the extra helix. (C) Region of the structure highlighted by the box in (A) showing the hydrophobic contacts made by helix-1 with helices 3 and 4. (D) Top down view of (B). (E) The thermal denaturation profiles for the talin rod polypeptides; profiles are shown for the 4-helix module (squares) and the 5-helix bundle (circles).