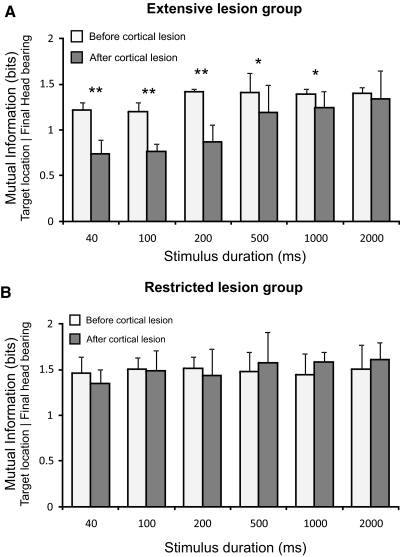
Fig. 5.
Mean and SD of the mutual information values between target location and final head bearing across sound duration for the extensive lesion (A) and restricted lesion (B) groups both before (white bars) and after (gray bars) the cortex had been aspirated. In contrast to the percent correct responses in the approach-to-target task, the MI values for the prelesion data were relative constant across sound duration. Extensive cortical lesions caused a significant reduction of the MI values for sounds of <500 ms in duration (A), whereas restricted cortical lesions did not alter the MI values (B). **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05.