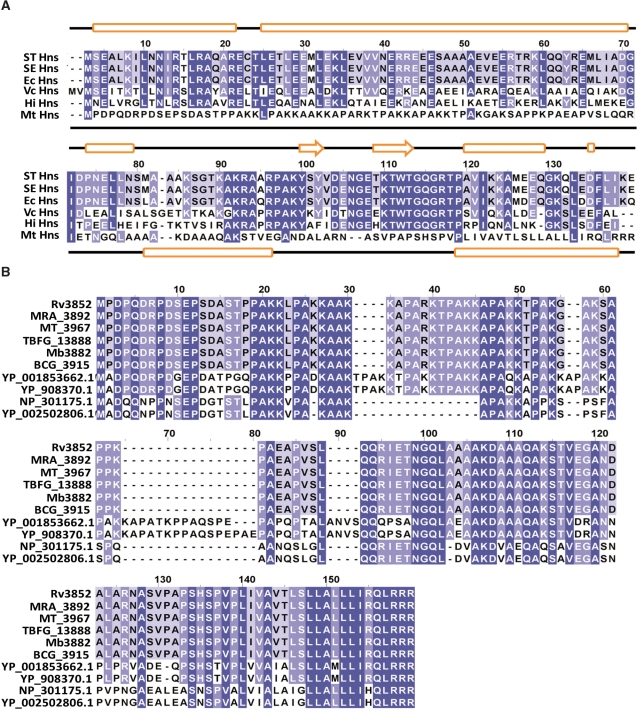
Figure 1.
ClustalW alignment of H-NS homologues from various bacterial species. (A) Alignment of amino acid sequences of H-NS homologues include the following: STHns, S. typhimurium LT2 SGSC1412 Hns (STM1751), SEHns, S. enterica serovar Typhi Ty2 Hns (t1662), EcHns, Escherichia coli Hns (b1237), VcHns, V. cholerae El Tor N16961 Hns (VC1130), HiHns, Haemophilus influenzae 86028NP (NTHI1464) and MtHns, Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv Hns (Rv3852). Dark blue shading indicates identical amino acid residues; whereas, light blue indicates identical residues among the specified species. Secondary structure assignments for E. coli and M. tuberculosis H37Rv Hns proteins were carried out using the Jpred program (75) (http://www.compbio.dundee.ac.uk/∼www-jpred/) and are displayed above and below the alignments, respectively. The predicted secondary structures (cylinders represent alpha helices, arrows represent beta strands and lines represent loops, respectively) of E. coli and M. tuberculosis H-NS are shown at the top and bottom of the plot, respectively. (B) Amino acid sequences of M. tuberculosis H37Rv Hns (Rv3852), M. tuberculosis H37Ra Hns (MRA_3892), M. tuberculosis CDC1551 Hns (MT_3967), M. tuberculosis F11 Hns (TBFG_13888), M. bovis subsp. bovis AF2122/97 Hns (Mb3882), M. bovis BCG str. Pasteur 1173P2 Hns (BCG_3915), M. marinum M Hns(YP_001853662.1), M. ulcerans Agy99 Hns (YP_908370.1), M. leprae TN Hns (NP_301175.1) and M. leprae Br4923 Hns (YP_002502806.1) were aligned using ClustalW2 and the resulting alignment was viewed using Jalview 2.4.0.b2 (76). Dark blue shading indicates identical amino acid residues in all the species; whereas, light blue indicates identical residues among the specified species.