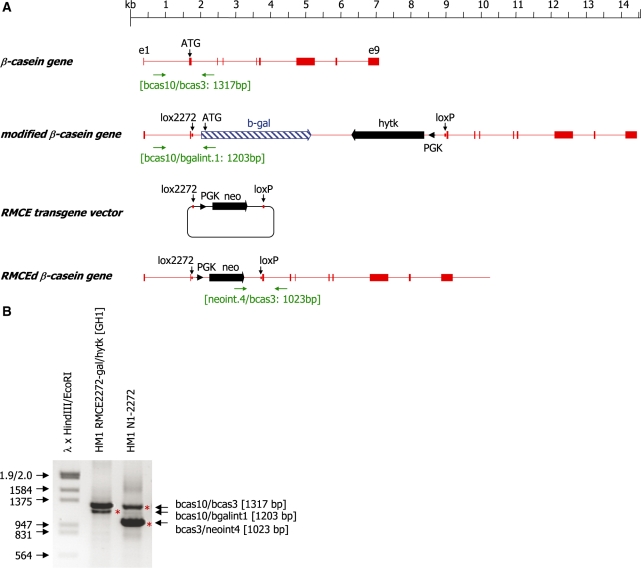
Figure 1.
(A) Schematic representation of the murine β-casein gene and its derivatives after homologous recombination and RMCE. Exons of the β-casein gene are indicated as solid boxes, the neomycin (neo) and hytk selection marker genes are indicated as solid arrows, respectively and the β-galactosidase gene (β-gal) is indicated as a hatched arrow. The PGK promoter elements directing expression of the selection marker genes are indicated as black arrowheads. The positions of the lox2272 and loxP sites and the translational start codon (ATG) are marked by vertical arrows. The primer binding sites (horizontal arrows) used for genotyping and the sizes of the expected PCR products are indicated. (B) PCR analysis of genomic DNA isolated from the cell clones HM1 RMCE2272-gal/hytk (GH1), and the cell clone HM1 N1-2272 derived from it. A 1317-bp band is detected in both samples and represents the unmodified β-casein allele. HM1 RMCE2272-gal/hytk (GH1) cells carry an insertion of a β-galactosidase open reading frame and a PGK-hytk expression cassette at one of the β-casein alleles as indicated by the occurrence of a 1203-bp PCR product. Cell clone HM1 N1-2272 was derived after an RMCE event which exchanged the β-gal and hytk genes for the neo selection marker gene. The correct modification is indicated by the generation of a 1023-bp PCR product and the concomitant loss of the 1203-bp band. Phage λ DNA digested with HindIII and EcoRI was used as molecular weight marker.