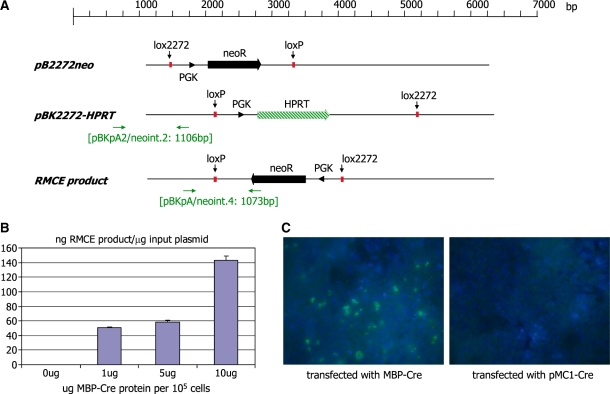
Figure 2.
(A) Schematic representation of the plasmids pB2272-neo and pBK2272-HPRT. The neomycin resistance marker genes (neo) are indicated as solid arrows. The PGK promoter is indicated as an arrowhead. The HPRT selection marker gene is indicated as a striped arrow. The primer binding sites (horizontal arrows) used for genotyping and the sizes of the expected PCR products are indicated. (B) Quantitative PCR analysis of recombinase mediated cassette exchange in HEK 293 cells. Cells were transfected with equimolar amounts of the plasmids pBK2272-HPRT and pB2272-neo. Twenty four hours post-plasmid transfection the cells were transfected with different amounts of an MBP-Cre fusion protein using the Proteo-Juice reagent (Novagen). DNA was isolated from cells 36 h later and analysed by real-time PCR using the primer pair neoint.2/pBKpA2 (yielding a 1106-bp fragment) to quantify the concentration of the input plasmid pBK-2272HPRT and the primer pair neoint.4/pBKpA (yielding a 1073-bp fragment) to quantify the concentration of RMCE product generated. The concentrations are presented as pg RMCE product per ng input plasmid in correlation with the amount of MBP-Cre protein transfected into 1 × 105 cells. (C) Immunohistochemistry of cells transfected with the plasmids pB2272-neo and pBK2272-HPRT and the protein MBP-Cre (or the plasmid pMC1-Cre; right panel). The MBP section of the protein was detected using a 1 : 200 dilution of an MBP-specific rabbit antiserum and a goat-anti-rabbit FITC-linked secondary antiserum.