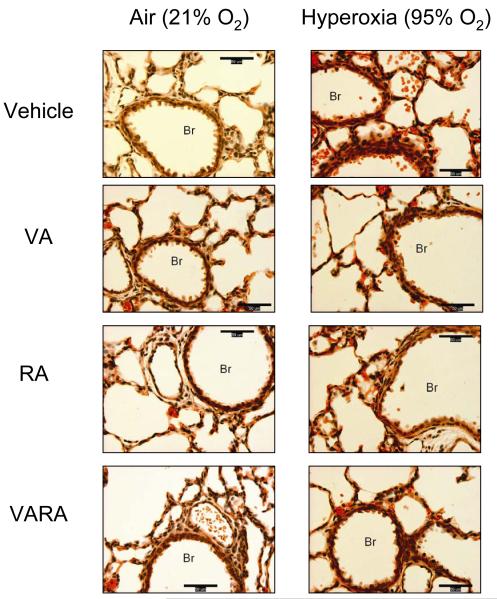
Figure 2. Photomicrographs of lungs from neonatal mice exposed to room air or hyperoxia while being treated with vehicle (Veh), vitamin A (VA) alone, retinoic acid (RA) alone, or vitamin A + retinoic acid (VARA).
(H&E stain; 400x; calibration bar = 50 μm; Br = Bronchus). Exposure to hyperoxia led to hemorrhage (erythrocytes within alveoli and in alveolar septae) and airway epithelial injury (denuded epithelial cells within Br) that were attenuated with VA, RA, and to a greater extent with VARA.