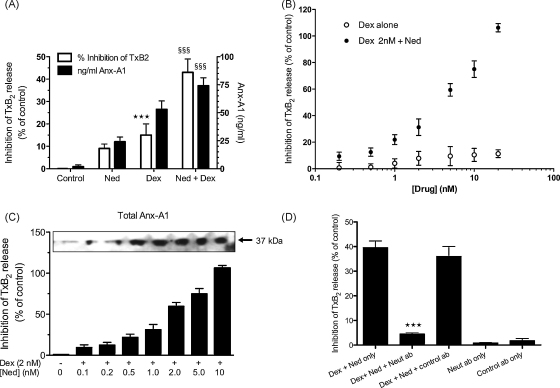
Fig. 3.
Nedocromil potentiates dexamethasone inhibition of TxB2 release from U937 cells. (Panel A) Measurement of TxB2 generation (left hand Y-axis) and Anx-A1 (right hand Y-axis) by ELISA assay in the medium of U937 cells after treatment with nedocromil (5 nM), dexamethasone (2 nM), or a combination of both. The varying inhibition of TxB2 release corresponds with the amount of Anx-A1 externalised. ***P < 0.001 relative to control values; §§§P < 0.001 relative to dexamethasone alone values. (Panel B) Dexamethasone itself (0.2–20.0 nM) inhibits TxB2 release at 5 min (as assessed by ELISA assay) but does not produce a maximal effect. However, when nedocromil (0.05–20 nM) is added to a maximally effective (2 nM) concentration of dexamethasone, a concentration-dependent potentiation of the inhibitory effect occurs with near maximal inhibition achieved at 20 nM nedocromil. (Panel C) The inhibition of TxB2 release (as assessed by ELISA assay) by escalating concentrations of nedocromil (0.2–10 nM) in the presence of a fixed concentration (2 nM) of dexamethasone is paralleled by increasing amounts of Anx-A1 externalised from U937 cells. Insert: representative Western blot in which the total Anx-A1 in the medium was assessed. (Panel D) Reversal of the TxB2 inhibitory action of a combination of 2 nM dexamethasone with 0.5 nM nedocromil by a mouse anti-Anx-A1 neutralising monoclonal antibody (mab 1A) but not by an irrelevant isotype matched monoclonal antibody. ***P < 0.001 relative to dexamethasone + nedocromil values. All experiments were done at least three times and the blot is representatives from one of these experiments. Densitometry was performed as described in the methods and the optical density units normalised by comparison to α-tubulin. Data are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. Statistical differences between groups were established using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Bonferroni post hoc test.