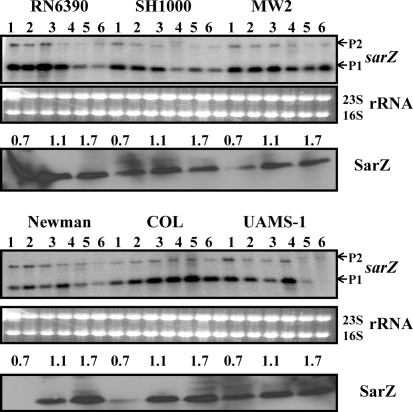
Fig. 4.
Expression of the sarZ gene in the different wild-type strains at various phases of growth. Northern blots were hybridized with 550 bp DNA fragments containing the coding region of the sarZ gene. A total of 10 μg cellular RNA was loaded in each lane. Lanes 1–6, total cellular RNA from the growing cultures at OD600 0.3, 0.7, 1.1, 1.4, 1.7 and overnight (stationary) (Fig. 1b). P1 and P2 indicate the major (0.55 knt) and minor (1.5 knt) transcripts of the sarZ locus (Ballal et al., 2009). The region containing the 23S and 16S rRNA of the ethidium bromide-stained gel used for blotting is shown as a loading control. The third and sixth panels from the top represent Western blots of intracellular extracts from the different wild-type strains probed with anti-SarZ polyclonal antibodies. Equivalent amounts of extracts (20 μg) from the different phases of growth (OD600 ∼0.7, early exponential; OD600 ∼1.1, exponential; OD600 ∼1.7, post-exponential) were used to detect SarZ expression.