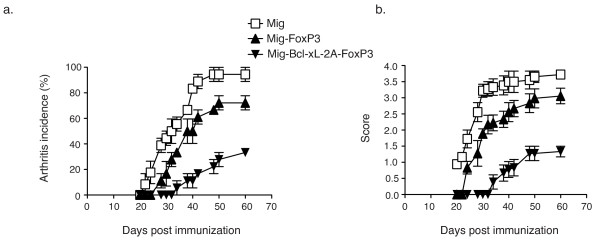
Figure 5.
Adoptive cell transfer of FoxP3- and Bcl-xL-transduced regulatory T cells suppresses collagen-induced arthritis (CIA). Naive CD4+ T cells from DBA/1J mice were stimulated with anti-CD3 plus anti-CD28 antibodies. On days 2 and 3, the cells were transduced with retroviral constructs: vector (Mig), FoxP3 (Mig-FoxP3), or FoxP3 with Bcl-xL (Mig-Bcl-xL-2A-FoxP3). On day 6, green fluorescent protein-positive (GFP+) T cells were sorted and prepared for adoptive cell transfer. CIA was induced in male DBA/1J mice (>4 months old) by one (day 0) intradermal immunization in the base of the tail with 100 μg of bovine type II collagen in complete Freund's adjuvant, containing 5 mg/mL killed Mycobacterium tuberculosis (H37Ra). On day 15 after the immunization, the mice received transduced GFP+ cells (2.5 × 106 per mouse, six mice per group). In the following days, the arthritis incidence (a) and clinical score (b) were evaluated by examining the paws and using a 4-point scale: 0, normal paw; 1, minimal swelling or redness; 2, redness and swelling involving the entire forepaw; 3, redness and swelling involving the entire limp; 4, joint deformity or ankylosis or both. Values are the mean ± standard error of the mean of data obtained in three experiments, and in each experiment, six mice per group were used. Summaries of the incidences and the mouse arthritis scores of the three experiments are listed in Additional files 1 and 2.