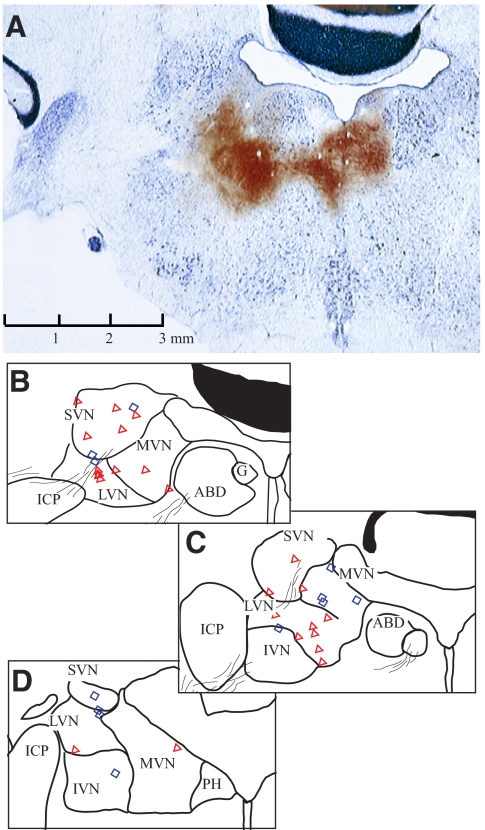
Fig. 2.
Anatomical locations of recorded vestibular neurons from one squirrel monkey. Cerebellum and brain stem were sectioned in the coronal plane of electrode penetration, tilting 22° dorsocaudally and 15° laterally with respect to the stereotaxic plane. The brain was sliced at 40 μm intervals. Every fourth section was stained with Perls/3,3′-diaminobenzidene (Perls/DAB, brown), whereas its next adjacent section was stained with thionine (blue). A: confirmation of recording sites with electrolytic lesions (see methods). Currents were injected at 2 sites, 2 mm apart, near the left abducens nucleus. The only one section where electrolytic lesions were revealed with Perls/DAB stain was superimposed on its adjacent section with thionine stain. B–D: line drawings, with reconstructed neurons' locations, of sections corresponding to A (B) and the following 2 sections at 0.48 (C) and 1.28 (D) mm caudal to A. Neurons located within 0.48 mm anterior/posterior to A–B are shown on B (symbols). Neurons at 0.5 to <1 mm caudal to A are superimposed on C, whereas those at 1–2.5 mm caudal are shown in D. Neurons are marked as simple (red triangle) or complex (blue diamond) types. Calibration in A applies to all sections. ABD, abducens nucleus; SVN/MVN/LVN/IVN, superior/medial/lateral/inferior vestibular nucleus; ICP, inferior cerebellar peduncle; G, genu of facial nerve; PH, nucleus prepositus hypoglossi.