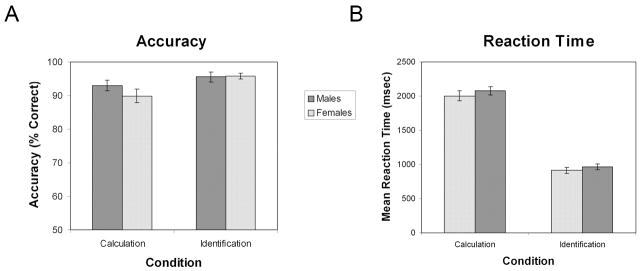
Figure 1. Mental arithmetic task performance in males and females.
(A) Accuracy as a function of gender (male, female) and condition (Calculation, Identification). No significant difference between genders was found in either the Calculation or Identification conditions, and there was no significant interaction between gender and condition. In both males and females, accuracy was significantly greater in the Identification, compared to the Calculation, condition. (B) Reaction time as a function of gender and condition. No significant difference between genders was found in either the Calculation or Identification conditions, and there was no significant interaction between gender and condition. In both males and females, reaction time was significantly greater in the Calculation, compared to the Identification, condition.