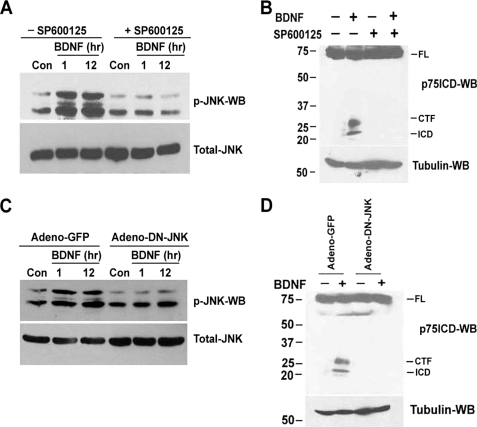
FIGURE 2.
Inhibition of JNK activation blocks BDNF-induced p75NTR cleavage in sympathetic neurons. A and B, sympathetic neurons from P4 rats cultured and maintained for 2 days in 20 ng/ml NGF, were rinsed to remove the NGF and refed with medium containing 12.5 mm KCl, to promote survival. The neurons were treated for 1 h with 10 μm of the JNK inhibitor SP600125, and then treated with 200 ng/ml BDNF for 1 or 12 h (A). For p75NTR cleavage, the neurons were treated with 10 μm ZLLLH in the presence and absence of JNK inhibitor SP600125 (10 μm) with or without the addition of 200 ng/ml BDNF for 12 h (B). Then neurons were lysed and subjected to Western blot analysis using antibodies to phospho-JNK (p-JNK), total-JNK (A), p75NTR ICD, or tubulin (B). C and D, sympathetic neurons were infected with an adenovirus expressing GFP (Adeno-GFP) or DN-JNK (DN-JNK). 24 h later the neurons were rinsed to remove NGF and refed with medium containing 12.5 mm KCl with or without the addition of 200 ng/ml BDNF for 1 or 12 h (C) or treated with 10 μm ZLLLH with or without the addition of 200 ng/ml BDNF for 12 h (D). Lysates were subjected to Western blot analysis using phospho-JNK, total-JNK (C), and p75NTR ICD and tubulin (D) antibodies. The full-length receptor (FL), CTF, and the ICD are indicated. Data are the representative of three independent experiments.