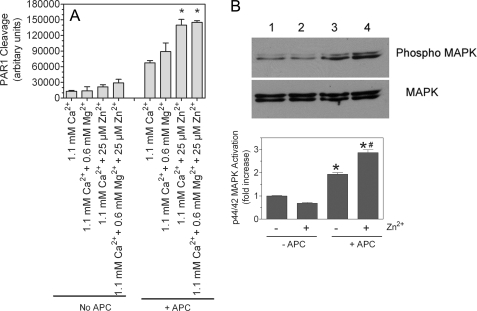
FIGURE 10.
Effect of physiological concentrations of Zn2+ and Mg2+ on PAR1 cleavage of APC and downstream p44/42 MAPK activation. A, HUVEC monolayers were transduced with AP-PAR1 adenovirus (20 multiplicity of infection/cell) and allowed to grow for 48 h. HUVEC monolayers expressing AP-PAR1 were treated with APC (80 nm) in the presence and absence of physiological concentrations of Ca2+, Mg2+, or Zn2+ alone or in combination. A small aliquot of the supernatant was removed immediately after adding APC and after 45 min, and AP activity in the supernatant was measured as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The basal readings obtained at 0 min were subtracted from the readings obtained at 45 min. The data shown in the graph represent the means ± S.E. (n = 3). *, the value is significantly higher than the value obtained in the reaction mixture containing the corresponding concentration of Ca2+ alone (p < 0.005). B, confluent monolayers of HUVEC were serum-starved in the presence and absence of 25 μm Zn2+ for 3 h in serum-free medium, which contains near physiological concentrations of Ca2+ (1.8 mm) and Mg2+ (0.8 mm). Thereafter, APC (20 nm) was added to the cells for 15 min. The cell lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with MAPK antibodies. The band intensities were calculated with Quantity One software of four independent experiments and presented as the means ± S.E. (n = 4). *, the value is significantly higher (p < 0.05) compared with the corresponding value obtained in the absence of APC. #, APC-mediated p44/42 activation is significantly higher (p < 0.05) in the presence of Zn2+ compared with in its absence.