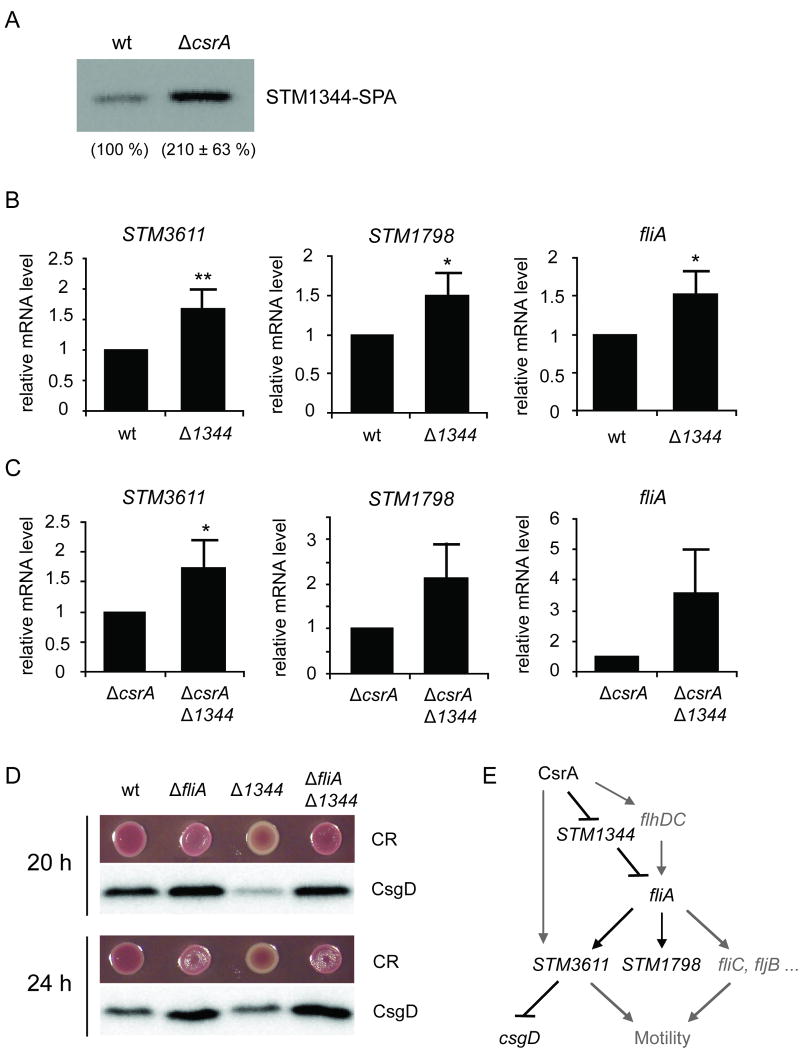
Figure 5.
CsrA-mediated regulation of STM1344 and its downstream effects. A) Protein levels of SPA-tagged STM1344 in the wild type (wt) and the csrA deficient background (ΔcsrA). The bacteria were grown at 37 °C to OD600 1.5. B) Effect of a mutation in STM1344 (Δ1344) on the mRNA levels of STM3611, STM1798 and fliA measured by quantitative Real-Time RT PCR, after growth of the bacteria at 37 °C to OD600 1.5. The values represent means with standard deviations (** P < 0.01; * P < 0.05). C) Effect of a double mutation in csrA and STM1344 (ΔcsrA Δ1344) on the mRNA levels of STM3611, STM1798 and fliA. The values represent means with standard deviations (* P < 0.05). D) STM1344 regulates rdar morphotype expression and CsgD levels through fliA. Rdar morphotype expression and CsgD protein levels were analysed in the wild type UMR1 and its isogenic mutants in fliA, STM1344 and fliA STM1344. The bacteria were grown for 20 h or 24 h, respectively, at 28 °C on Congo Red (CR) LB agar plates without salt. E) Schematic model depicting the regulation of STM3611 by STM1344 through fliA. The model illustrates that CsrA controls the flagella cascade at multiple levels, through FlhDC, STM1344 and STM3611.