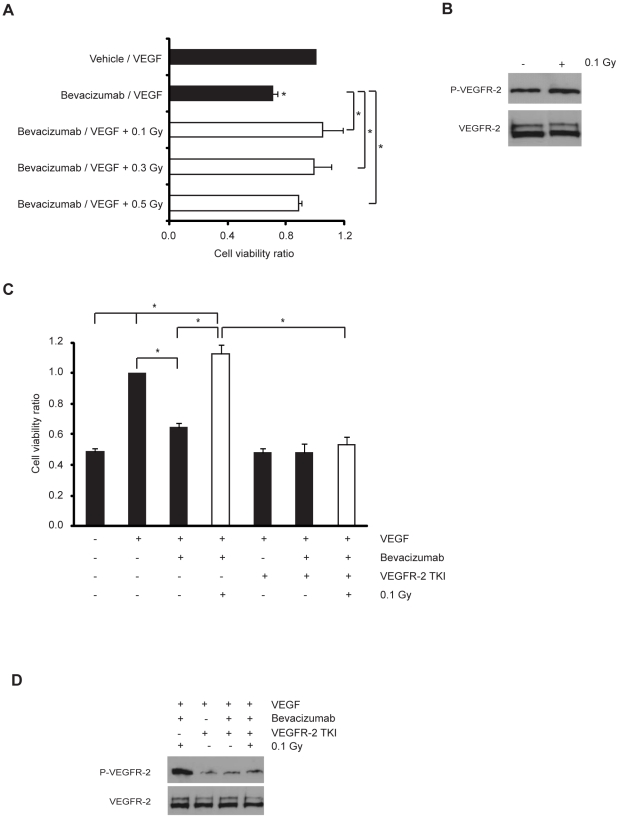
Figure 3. Low-dose IR protects microvasculature from bevacizumab-induced cell death by inducing VEGFR-2 activation.
(A) Cells were cultured without serum for 12 h and incubated with vehicle/VEGF (20 ng/ml) or bevacizumab (0.25 mg/ml)/VEGF (20 ng/ml) mixtures. Then, cells were exposed or not to 0.1, 0.3 or 0.5 Gy and the percentage of apoptotic cells was assessed by flow cytometry at 48 h post-irradiation. Data (means ± s.d.) represent the ratio between cell viability percentage of each experimental condition and control condition and are derived from four independent experiments. (B) Representative blots from four independent experiments. Cells were exposed or not to 0.1 Gy. Western blot analysis of total- and phospho-VEGFR-2. (C) Cells were cultured without serum for 12 h and treated or not with VEGFR-2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI at 300 nM) for 2 h and stimulated or not with VEGF (20 ng/ml) or bevacizumab (0.25 mg/ml)/VEGF (20 ng/ml) mixture. Then, cells were exposed or not to 0.1 Gy. The percentage of apoptotic cells was assessed by flow cytometry at 48 h post-irradiation. Data (means ± s.d.) represent the ratio between cell viability percentage of each experimental condition and control condition and are derived from four independent experiments. * P<0.03. (D) Representative blots from four independent experiments. Western-blot analysis of total- and phospho-VEGFR-2 (P-VEGFR-2) of HMVEC-L cultured without serum for 12 h and treated or not with VEGFR-2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI at 300 nM) for 2 h and stimulated with VEGF (20 ng/ml) or bevacizumab (0.25 mg/ml)/VEGF (20 ng/ml) mixture. (B and D) The level of VEGFR-2 phosphorylation was assessed after 15 min post-irradiation.