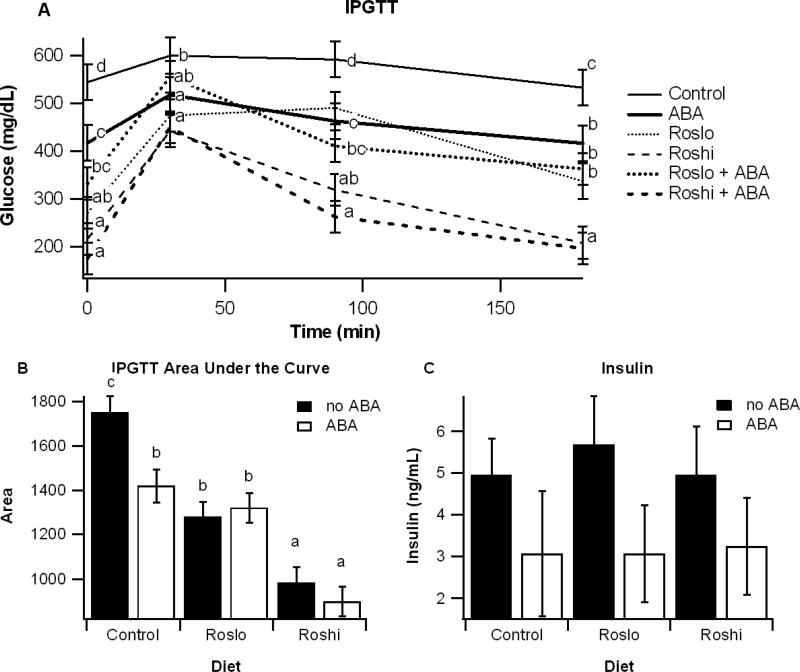
Figure 1.
Effect of abscisic acid (ABA) and rosiglitazone (Ros) on glucose tolerance and fasting insulin. Obese db/db mice were fed high-fat diets containing 0, 15, or 70 mg/kg diet rosiglitazone maleate (control, Roslo, and Roshi, respectively) with and without racemic ABA (100 mg/kg diet). On day 42 mice underwent an intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test (IPGTT) (A). Areas under the curve (B) were calculated for each treatment. On day 55 fasting insulin levels were measured for mice on each diet (C). Data are represented as mean ± standard error. Points with different subscripts are significantly different from each other (P<0.05).