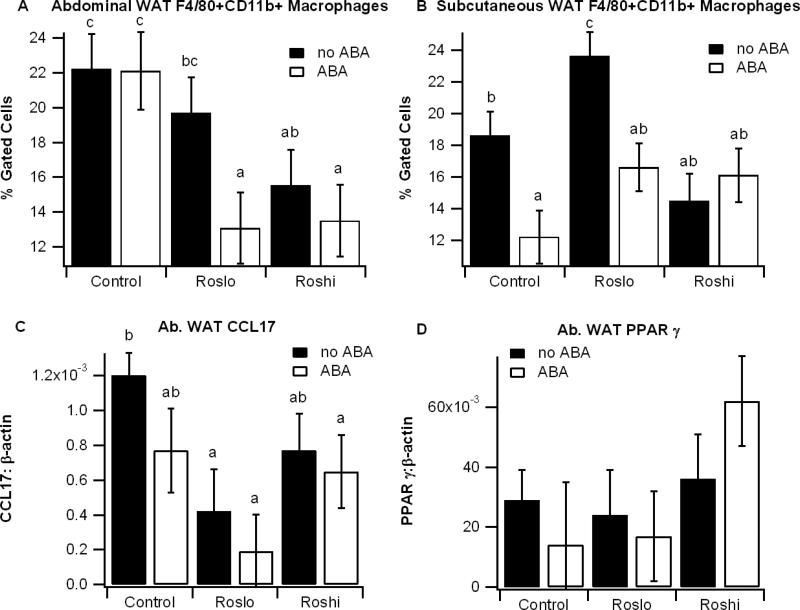
Figure 2.
Effect of abscisic acid (ABA) and rosiglitazone (Ros) on immune cell infiltration into white adipose tissue. Obese db/db mice were fed high-fat diets containing 0, 15, or 70 mg/kg diet rosiglitazone maleate (control, Roslo, and Roshi, respectively) with and without racemic ABA (100 mg/kg diet). On day 60 the percent of F4/80+CD11b+ in the stromal vascular fractions of abdominal white adipose tissue (Ab. WAT) (A) and subcutaneous WAT (B) were assessed by flow cytometry. The expressions of the M1 marker CCL17 (C) and peroxisome proliferator activated receptor γ (PPAR γ) (D) in Ab. WAT were calculated as a ratio to the housekeeping gene β-actin. Data are represented as mean ± standard error. Points with different subscripts are significantly different from each other (P<0.05).