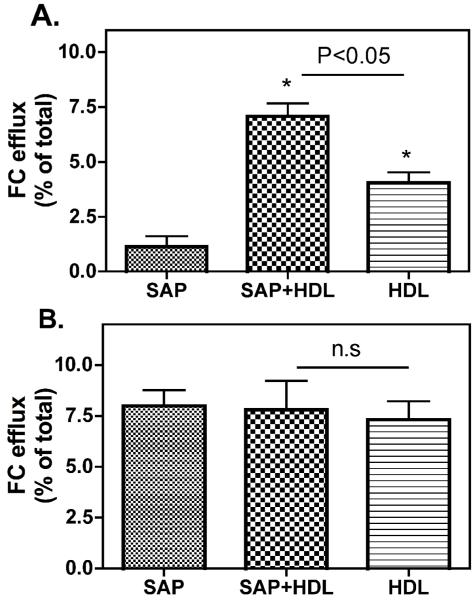
Figure 4. Effect of SAP on cholesterol efflux.
A. SR-BI-dependent cholesterol efflux to SAP. CHO-SR-BI and control CHO-A7 cells were labeled with 0.2 μCi/ml [3H]cholesterol for 48 h, equilibrated in cholesterol free medium for 16 h, and then incubated with SAP, SAP + HDL3 or HDL3 at 37 °C for 5 h to determine cellular efflux as described in “Material and Methods”. Efflux of free cholesterol into the media is expressed as percentage of the total radioactivity in the media and cells. The efflux values were subtracted from blank values obtained by incubating cells with albumin containing efflux medium. SR-BI-specific values were calculated as the difference between the efflux values in CHO-SRBI cells and control CHO-A7 cells. Values shown are mean ± SD of triplicate determinations. B. ABCA1-dependent cholesterol efflux in macrophages. J774 cells were labeled with 0.2 μCi/ml [3H]cholesterol in medium for 48 h. Cellular ABCA1 expression was stimulated by incubation of J774 cells with 0.3mM of cAMP for 16 h. Efflux experiments were performed at 37 °C by incubating cells with different ligands for 16 h. The efflux values were subtracted from blank values obtained by incubating cells with albumin containing efflux medium. ABCA1-specific efflux was calculated by the difference between J774-cAMP and J774 cells. Values shown are mean ± SD of triplicate determinations.