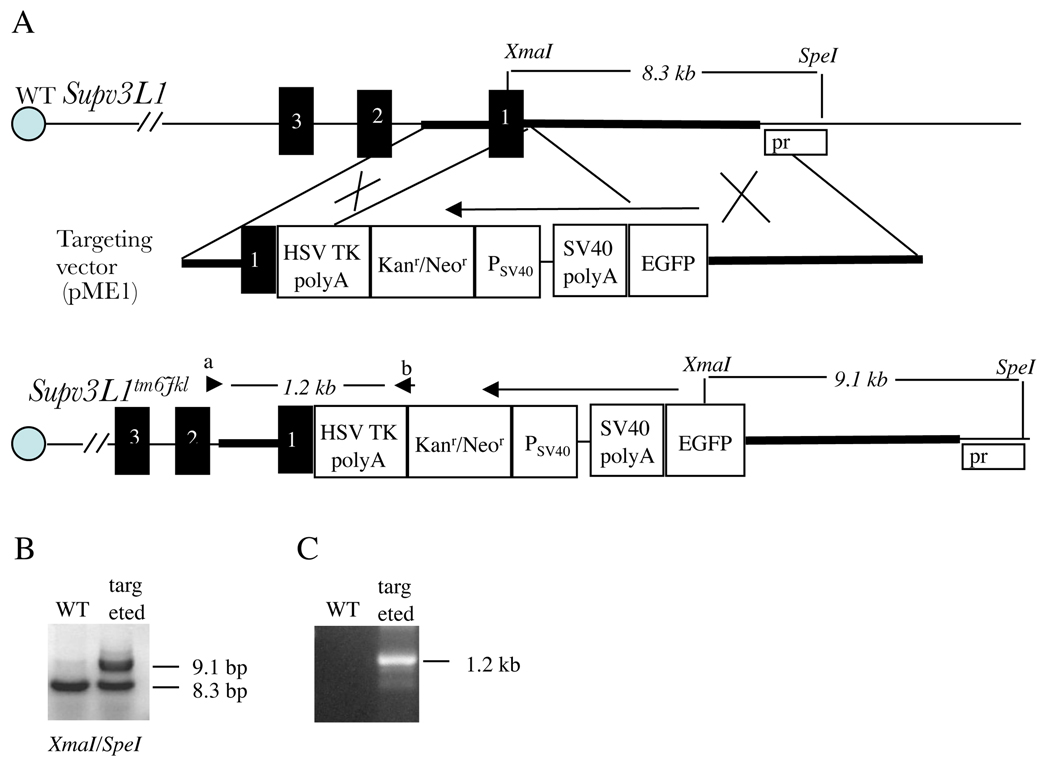
Figure 1.
Generating the knock-in EGFP allele (Supv3L1tm6Jkl). (A) Genomic structure of the wild-type Supv3L1 locus, targeting vector, and allelic modification generated in this study. Regions of homology between the genomic sequence and the vector are shown in bold. XmaI, XmaI restriction site; SpeI, SpeI restriction site; Pr, probe used in Southern blotting; EGFP, enhanced green fluorescent protein coding sequence; SV40 polyA, SV40 polyadenylation signals; PSV40, SV40 promoter; Kanr/Neor, neomycin/kanamycin resistance gene of Tn5; HSV TK polyA, polyadenylation signals from the Herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase (HSV TK) gene. Black boxes represent the first three exons of Supv3L1 (composed of total 16 exons). Arrows indicate the direction of transcription. Arrowheads designate the positions of PCR primers. (B) Southern hybridization analysis of targeted ES cells showing a correct integration event at the 5’ arm. Probe was generated by PCR using genomic DNA and primer pair c + d (ATGTCCGCACGCTGCGACTGTCGTCAGCC and GGCTGACGACAGTCGCAGCGTGCGGACAT). (C) PCR analysis of a targeted ES cell clone using primers a+b (CACGGCACTGCGTGCTTGGCAAGGCATAT and GACAGAATAAAACGCACGGTGTTGGGTCGT) confirming correct integration event at the 3’ arm.