Fig. 3.
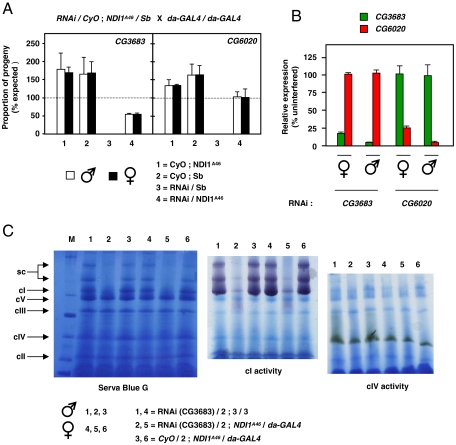
NDI1 can compensate for complex I deficiency in Drosophila in vivo. (A) Mean proportions of each progeny class (± SD, 2 replicate experiments) expressed as percentages of expected proportion eclosing from crosses as shown. RNAi knockdown targets were CG3683 (n = 423 total progeny) and CG6020 (n = 673 total progeny). In absence of NDI1 knockdown was lethal in both cases (class3). See also Fig. S3 D and E. (B) Verification of knockdown at RNA level by Q-RT-PCR. Data normalized to target gene expression level in progeny from the same cross lacking interfering RNA (for full data, see Fig. S3F). (C) Verification of knockdown at the protein level. BNE gels of mitochondrial protein extracts, stained as indicated (cI-V—complex I-V, sc—supercomplexes). Knockdown of CG3683 (here) or CG6020 (Fig. S3H) in NDI1-rescued flies gave almost complete absence of assembled, active complex I.