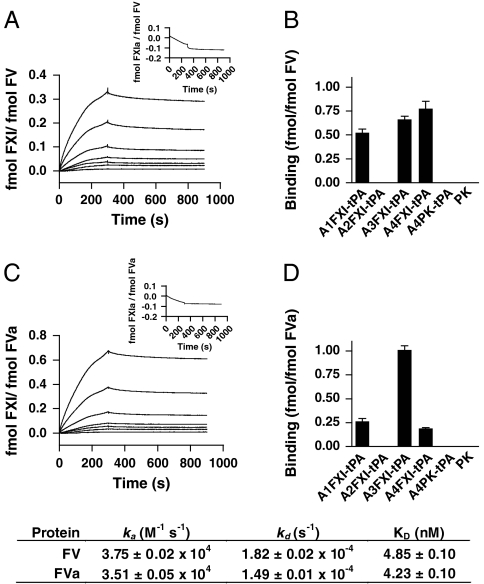
Fig. 3.
Factor XI binds to factor V(a) with high affinity via multiple binding sites. Surface plasmon resonance studies were performed with either FV or FVa immobilized on C1 sensor chips. Binding of FXI (0, 3.1, 6.3, 12.5, 25, 50, 100 and 200 nM) to immobilized FV (A) or FVa (C) was assessed at a flow rate of 50 μL/ min at 25 °C. No binding of FXIa (100 nM) to either FV or FVa was observed (insets). Domains responsible for the interaction between FXI and FV (B) or FVa (D) were mapped with individual tPA-tagged apple domains of FXI (25 nM), designated A1FXI-tPa to A4FXI-tPA. Binding of constructs to immobilized FV or FVa was assessed as described in Materials and Methods. PK and its tPA-tagged apple4 domain (A4PK-tPA) served as controls. Data are expressed as mean ± SD in fmol bound analyte (FXI, PK, or construct) per fmol immobilized ligand (FV or FVa). Inset shows the obtained association (ka) and dissociation (kd) rates ± SD, as well as the affinity constants (KD) ± SD for the interaction between FXI and FV or FVa. All binding experiments were performed at least three times. Representative SPR traces are shown.