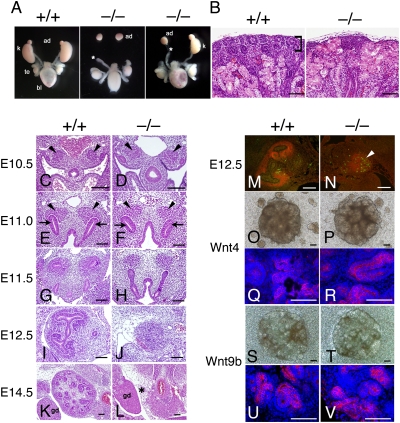
Fig. 2.
Kidney agenesis and impaired ureteric bud attraction in Kif26b-null mutants. (A) Urogenital tissues from wild-type (Left) and Kif26b-null (Center and Right) newborn mice. ad, adrenal gland; k, kidney; te, testis; bl, bladder. Asterisk, blind-ended ureter. (B) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of a wild-type kidney and a mutant remnant kidney in newborn mice. Square bracket, mesenchyme in the cortical nephrogenic zone. (Scale bars, 100 μm.) (C–L) Failure of ureteric bud attraction under Kif26b deficiency. Wild-type and Kif26b-null embryonic kidneys were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Arrowheads, metanephric mesenchyme; arrows, ureteric buds; gd, gonad; asterisk, remnant kidney. (M and N) Cleaved caspase-3-positive cells (arrowhead) in the Sall1-positive mesenchyme in Kif26b-null embryos at E12.5. Sections were immunostained for Sall1 (red) and cleaved caspase-3 (green). (Scale bars, 100 μm.) (O–R) Intact potency for epithelial conversion of the Kif26b-null mesenchyme. Metanephric mesenchyme was cultured on 3T3 cells expressing Wnt4. The samples shown in Q and R were stained with an anti-E-cadherin antibody and DAPI. (Scale bars, 100 μm.) (S–V) Metanephric mesenchyme was cultured on L-cells expressing Wnt9. The samples shown in U and V were stained with an anti-E-cadherin antibody and DAPI. (Scale bars, 100 μm.)