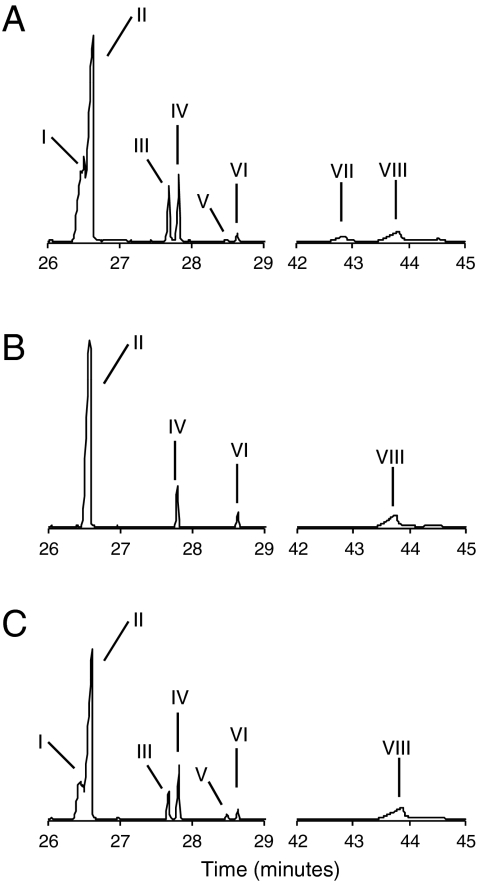
Fig. 2.
GC-MS total ion chromatograms of acetylated total lipid extracts of R. palustris cultures. The ΔhpnP mutant does not produce any C-2 methylated hopanoids. (A) R. palustris TIE-1. (B)R. palustris ΔhpnP. (C) R. palustris ΔhpnP complemented with the hpnP gene on a self-replicating plasmid. Numbered compounds: I, 2-methylhopenes; II, hopenes; III, 2-methyldiplopterol; IV, diplopterol; V, 2-methyltetrahymanol; VI, tetrahymanol; VII, 2-methylbacteriohopanetetrol; and VIII, bacteriohopanetetrol. Acetylated total lipid extracts were analyzed by high temperature GC-MS and compounds were identified by comparison of retention times and mass spectra to authentic compounds and published mass spectra (Table S6). Peak II is a co-elution of two hopene structures, hop-22(29)-ene and hop-21-ene. No methylated hopanoids eluted between 29–42 min (full chromatogram shown in Fig. S1). The complemented ΔhpnP strain did produce 2-methylbacteriohopanetetrol (compound VII) as verified by analysis of the 205 Da mass chromatogram and the mass spectrum; however, the peak is too broad to be seen at the resolution of this figure of the GC-MS total ion current.