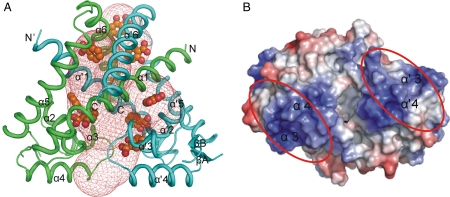
Fig. 1.
Overall structure of apo TcaR. (A) The overall structure of the TcaR homodimer. The protein structure is shown as a ribbon diagram with chain A in green and chain B in cyan. In addition, we used the program to explore possible cavities in TcaR for ligand binding. The cavities identified by CAVER are shown in mesh representation and using a solvent probe of radius 2 Å. In addition, the binding positions of eight salicylate molecules in the TcaR–salicylate complex are shown in sphere, revealing that the porous structure of TcaR is able to interact with numerous small molecules. (B) The DNA-binding domains. The electrostatic surface of the dimer is viewed after a rotation of approximately 90° from (A), with a horizontal axis in the plane of paper. The electrostatic surfaces are drawn either blue for positive or red for negative. Possible domains involved in binding DNA are labeled as red ovals.