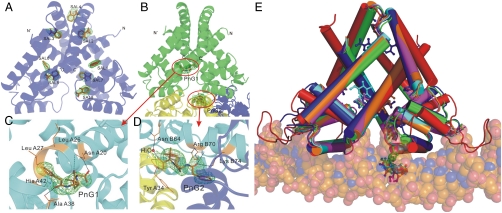
Fig. 3.
The structures of TcaR–ligand complex. (A) A ribbon diagram of TcaR in complex with salicylate. Salicylate binds to eight distinct locations in the dimer. (B) A ribbon diagram of TcaR in complex with penicillin G (PnG). PnG binds to two distinct locations in the dimer, with one binding in the interface of three TcaR dimers in the asymmetric unit along the crystallographic c axis. The central TcaR dimer is shown in green, and the right and left dimers are shown in blue and yellow, respectively. (C) One PnG molecule, PnG1 is located in the binding pocket directly at the junction of the DNA-binding domain and the dimerization domain. (D) In the other PnG binding site (PnG2), a PnG molecule is identified at crystal contact between three TcaR molecules related by crystallographic symmetry. (E) Superimposition of the TcaR-DNA model with TcaR–ligand complexes. The TcaR complexes of Sal (blue), PnG (green), Amp (orange), Meth (magenta), and Kan (cyan) revealed a significant conformational change at the WH domain.