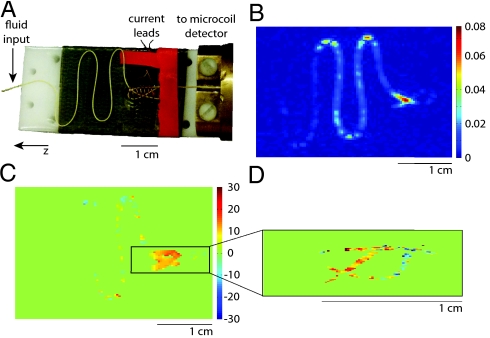
Fig. 5.
Remotely detected current-imaging experiments in (A) a serpentine flow phantom. Water flows in 150-μm PEEK tubing laid out in s-shaped curves, travels through a solenoid in which audio-frequency current encoding takes place and then flows into an optimized microsolenoid NMR detector. (B) A single time-of-flight image from a control experiment without current excitation. Images illustrating the phase accrued during current excitation and due to a resonant mechanism, relative to a control, are shown for (C) a nonselective experiment with FOVy = 2.41 cm and FOVz = 3.62 cm and for (D) a zoomed-in experiment that isolates a slice containing the coil, giving FOVy = 0.48 cm and FOVz = 1.45 cm. Images were taken with νcurrent = 400 Hz, τsl = 20 ms, and Vcurrent = 1.6 mV. All images have resolution 90 × 90 after zero filling by a factor of 2 and have comparable signal to noise.