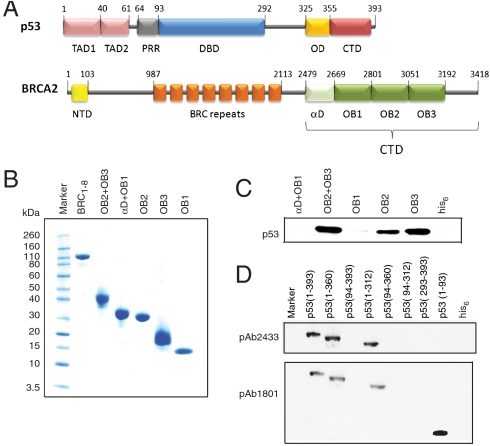
Fig. 1.
(A) Domain organization of p53 and BRCA2. The functional domains of p53 comprise an intrinsically unstructured transactivation domain TAD (1–93), specific DNA-binding core domain DBD (94–292), oligomerization domain (325–355), and C-terminal negative regulatory domain (362–293) (28). BRCA2 is a 3,418 amino acid protein consisting of an N-terminal transactivation domain (23–105), eight central BRC repeats of ∼30 amino acids each (987–2113), and a conserved C-terminal domain BRCA2CTD (2479–3152). The latter comprises an α-helical domain and three OB domains. (B) SDS-PAGE showing the purity of different BRCA2 domains used in pull-down experiments. (C) Interaction of p53 and BRCA2. Nickel pull-down of his-tag purified BRCA2CTD domains with flp53. Immunoblotting by using PAb1801 showed that OB2 + OB3, OB2, and OB3 interact with p53. *D) Nickel pull-down of truncated domains of p53 with his-tagged OB2 + OB3 construct of BRCA2. Immunoblots using PAb2433 (Abcam, specific for 277–296 aa of p53) and PAb1801 (Abcam, specific for 46–55 aa of p53) identified that OB2 + OB3 interacts with the transactivation domain of p53 (p53 TAD, 1–93).