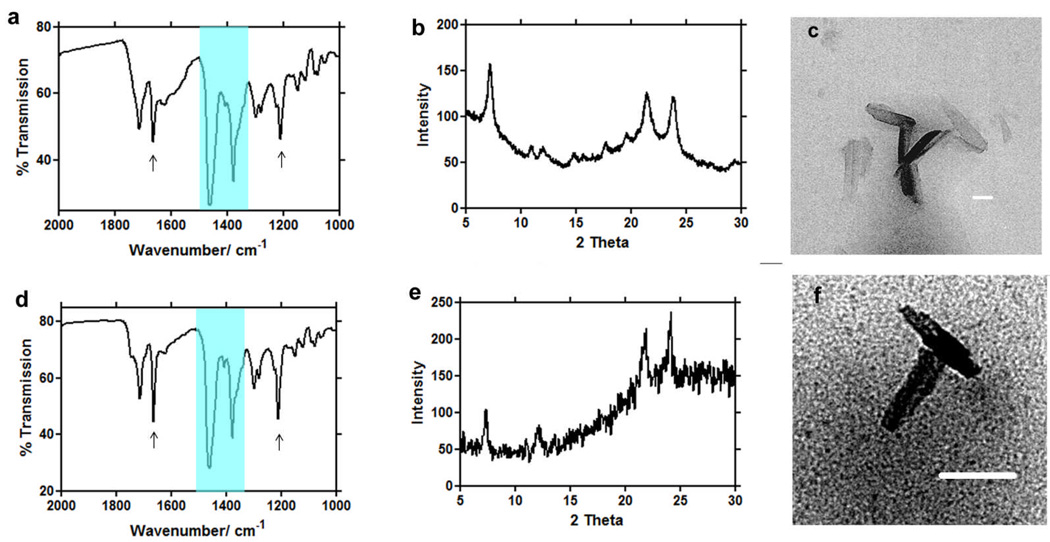
Fig. 3.
Infrared (IR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) evidence for the formation of β-haematin at the lipid-water interface using MSG (a, b, c), and MPG (d, e, f). Two large Nujol peaks (a, d) obscure the region between 1550 and 1320 cm−1 but do not interfere with the characteristic β-haematin IR peaks at 1660 and 1210 cm−1. Both products formed under mediation of MSG (a) and MPG (d) show IR characteristics of β-haematin. XRD of products obtained in presence of MSG (b) and MPG (e) show patterns characteristic of β-haematin39. TEM images of these products closely resemble haemozoin in their crystal habit (c, f). Scale bar = 50nm.