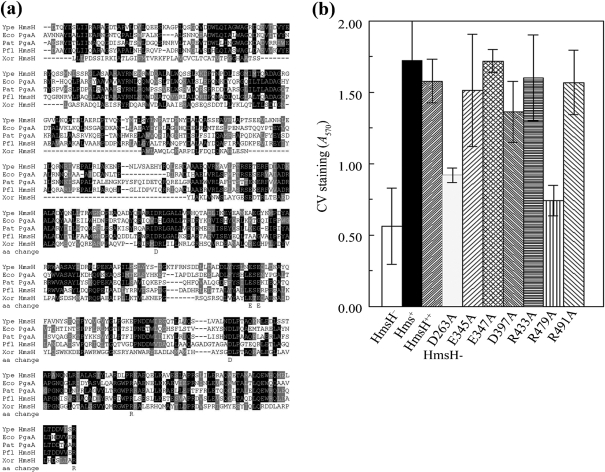
Fig. 4.
Analysis of changes in conserved residues in the N terminus of HmsH. (a) Alignment of these regions of HmsH and HmsH-like proteins from Y. pestis KIM10+ (Ype); P. fluorescens Pf-5 (Pfl); Pectobacterium atrosepticum SCR11043 (Pat; formerly Erwinia carotovora); E. coli K-12 substrain MG1655 (Eco); and X. oryzae KACC10331 (Xor). The black and grey boxes indicate residue identity and similarity, respectively. Sequences start with the first residue after the SignalP predicted signal sequence. The amino acid change line shows the amino acids individually changed to alanine. (b) Quantitative CV staining by Y. pestis cells expressing amino acid substitutions in the N-terminal region of HmsH. Controls are KIM6-2115 (in-frame ΔhmsH; HmsH−), KIM6+ (Hms+) and KIM6-2115(pNPM22) (HmsH++). Data shown are the mean of two or more independent experiments with duplicate samples from each trial. Error bars, sd. For clarity, the secondary mutation (D520A) and (D691A) in HmsH-E345A-D520A, HmsH-R433-D520A, HmsH-D397A-D520A and HmsH-R491-D691A is not shown in the labels.