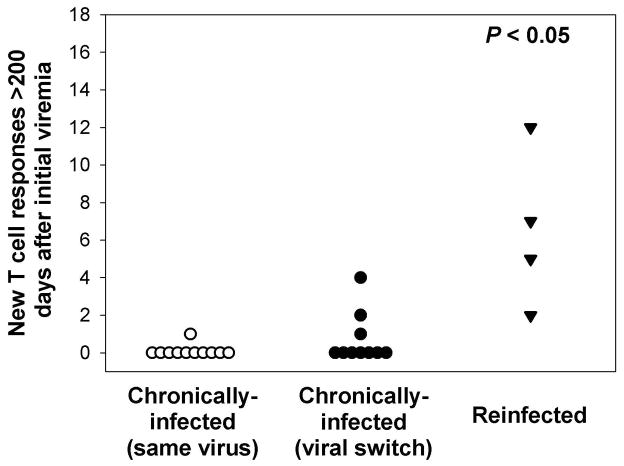
Figure 4.
Significantly greater numbers of new T cell responses are detected during reinfection than during chronic infection. Values represent new T cell responses in chronically-infected subjects in whom the same virus is detected during chronic infection, chronically-infected subjects in whom more than one genetically-distinct virus is detected during chronic infection, and reinfected subjects. A new T cell response was defined as a peptide that was recognized, in an IFN-γ ELISpot, by PBMCs obtained greater than 200 days following the first detection of viremia but not by PBMCs collected at earlier time points in reinfected subjects and chronically-infected individuals. P > 0.05 compared to both chronically-infected groups.