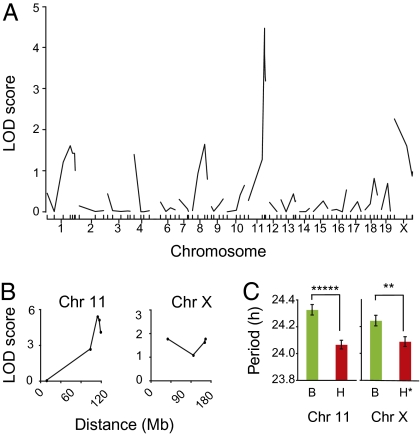
Fig. 2.
Genetic mapping of Clock suppressors. (A) Results of QTL analysis (single marker regression) with 55 [(C3H/HeJ × C57BL/6J)F1 × C57BL/6J]N2 animals. A significant association was detected with markers at the distal end of chromosome 11 (LOD = 4.7). A weak association was detected on chromosome X (LOD = 2.3). A significance threshold of LOD = 3.20 for P = 0.05 was determined by analysis of 1,000 permutation tests for this data set. (B) Examination of 41 additional Clock/+ N2 progeny confirms association of Clock suppression and loci on chromosomes 11 and X. Data shown represent 96 total N2 Clock/+ progeny. Peak associations occur with SSLP markers D11Mit12 on chromosome 11 (~113 Mb) and DXMit223 on chromosome X (~163 Mb). (C) Allelic effect of chromosome 11 (Left) and chromosome X (Right) on free-running period in 96 backcross Clock/+ mice. Data shown are mean ± SEM. A one-way ANOVA was significant for genotype at D11Mit12 on chromosome 11 [~113 Mb; ANOVA F(1,95) = 26.24, P = 1.67 × 10−6] and DXMit223 on chromosome X [~163 Mb; ANOVA F(1,95) = 8.33, P = 0.004). For chromosome 11, B stands for B6/B6 and H stands for B6/C3H genotypes. For chromosome X, B stands for either B6/B6 (female) or B6 (male) and H stands for either B6/C3H (female) or C3H (male).