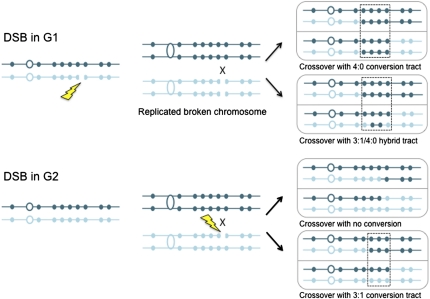
Fig. 1.
Gene conversion events associated with crossing over following G1- or G2-induced DSBs. A DSB in G1 is replicated, and both sister chromatids are repaired using the homolog nonsisters as templates; alternatively, one broken chromatid might repair first and then be used to template repair of the other broken sister chromatid. Repair of the breaks is accompanied by transfer of polymorphic markers from the undamaged to the broken chromatid, resulting in gene conversion (boxed area). Only one of the two repair events is associated with an RCO. If the same polymorphic markers are converted during both repair events, then a 4:0 tract will result; if one repair event involves more markers, a hybrid 4:0/3:1 tract will be formed. A G2 DSB would be expected to give rise to a RCO with no detectable gene conversion if the conversion tract is very short or to a 3:1 conversion. The homologs are shown in dark and light blue, respectively. The polymorphic sites are indicated by small solid circles, and the open circles represent the centromeres.