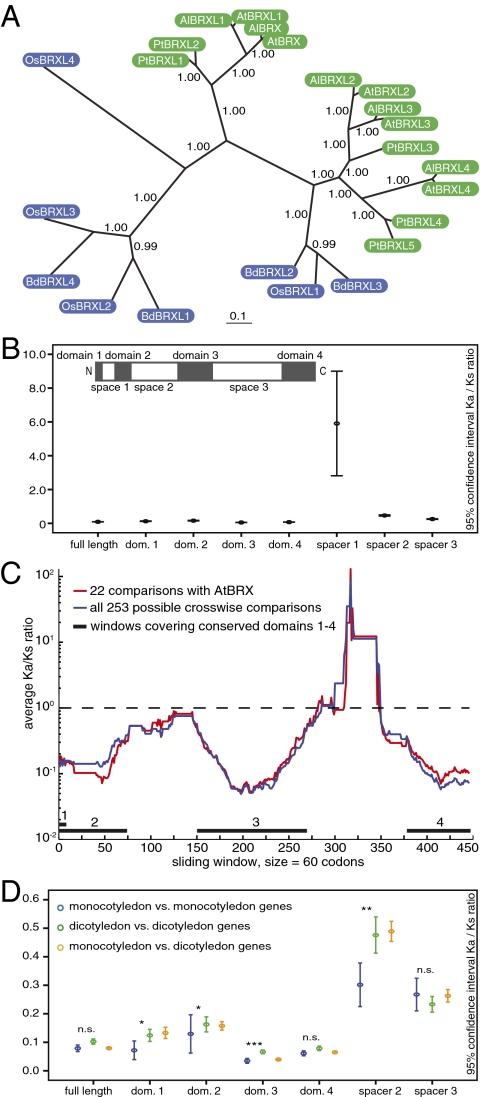
Fig. 1.
Phylogenetic and Ka/Ks analyses of BRX family genes. (A) Phylogenetic tree of BRX family genes from A. thaliana (At), A. lyrata (Al), poplar (Pt), rice (Os), and Brachypodium (Bd). Dicotyledon genes are depicted in green, monocotyledon genes in blue. (B) Ninety-five percent confidence interval Ka/Ks for all pairwise combinations of BRX family proteins, calculated for full-length coding sequence or individual conserved domains or spacer regions (see Inset schematic of BRX family protein structure, drawn to scale for AtBRX). (C) Ka/Ks calculated for pairwise combinations of BRX family proteins using a sliding window of 60 amino acids. Total length of the aligned amino acid sequences was 503. (D) Pairwise Ka/Ks calculated within mono- or dicotyledon proteins, or between the two groups. Significance is indicated for intergroup comparison between Ka/Ks of monocotyledon and dicotyledons. The outlier spacer 1 (Fig. S1) was removed for better viewing of the other ratios. dom., domain; n.s., not significant. *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001. Full statistics are given in Table S1.