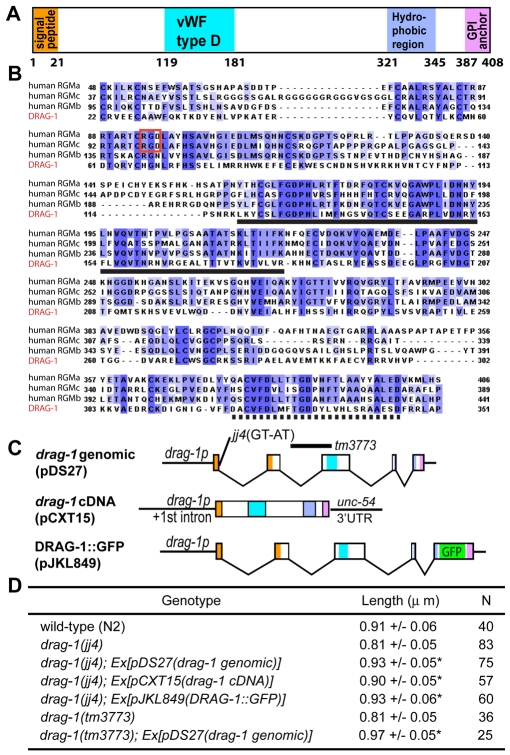
Fig. 3.
drag-1 encodes a putative GPI-anchor protein of the RGM family. (A) A schematic of the DRAG-1 protein, showing the various conserved motifs drawn in scale. (B) Alignment between DRAG-1 (the bottom line) and its human RGM homologs RGMa (GenBank AAI51133.1), RGMb (GenBank NP_001012779.2) and RGMc (GenBank NP_998818.1) in regions between the N-terminal signal peptide and the C-terminal pro-peptide. Notice the highly conserved vWF type D domain (solid underline) and hydrophobic region (dashed underline). The RGD motif (boxed in red) is present in RGMa and RGMc, but not in RGMb and DRAG-1. (C) Diagrams of the drag-1 genomic, cDNA and GFP-tagged constructs. The locations of the jj4 and tm3773 molecular lesions are shown. (D) Body size measurement of worms of various genotypes at 72 hours post-plating. Length is presented as the mean ± standard deviation. Asterisks indicate that the length of the drag-1 worms carrying a particular transgene is significantly different from that of the corresponding drag-1 single mutant. P<0.0001.