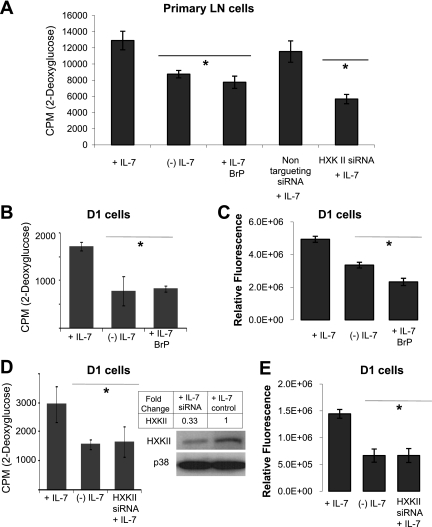
Fig. 6.
Inhibition of HXKII decreases glucose uptake and ATP levels independently of IL-7. A: LN T cells were cultured with 150 ng/ml of IL-7 for 7 days and then incubated with or without IL-7 (150 ng/ml) for 18 h and treated with either 3-bromopyruvate (BrP) or the Smart Pool HXKII small interfering RNA (siRNA; Accell) described below. A nontargeting siRNA was used as control. Glucose use was measured by assaying the uptake of 2-DOG as described in materials and methods. B: D1 T cells were incubated with IL-7 (50 ng/ml) or without IL-7 and BrP for 18 h, then assayed for glucose use with 2-DOG as described in materials and methods. C: D1 T cells were incubated with IL-7 (50 ng/ml) or without IL-7 and BrP as in B, and total cellular ATP was measured by using the rLuciferase/Luciferin reagent (Promega) in a luminometer as described in materials and methods. Shown are the values for relative fluorescence that correlate with ATP concentrations. D–E: HXKII gene expression was inhibited in D1 T cells using Smart Pool HXKII siRNA (Accell). Knockout of HXKII gene expression with specific HXKII siRNA is shown in the immunoblot for HXKII (D). p38 is included as a loading control. Relative densities of bands in the blot were determined by using ImageJ software. To assess glucose use upon HXKII inhibition, 2-DOG uptake was measured as described in materials and methods. E: total intracellular ATP was measured as described in C. Results are representative of 3 independent experiments performed in triplicate (values are average ± SD). *P < 0.05 compared with cells cultured + IL-7.