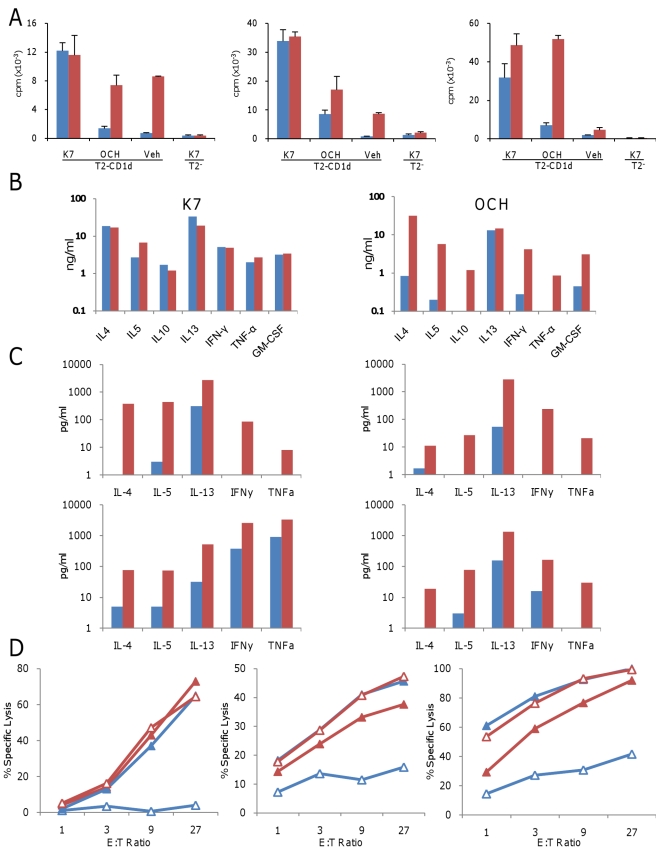
Figure 5. Differential autoreactive functional responses by human OCHHIGH and OCHLOW iNKT clones.
Matched pairs of human OCHHIGH (red columns and markers) and OCHLOW (blue columns and markers) iNKT clones were compared for their ability to proliferate, secrete cytokines, and exhibit cytotoxicity in response to lipid-pulsed or endogenous lipid presenting CD1d-positive antigen presenting cells. (A) Proliferation of three representative pairs of OCHHIGH and OCHLOW iNKT clones from different healthy donors in response to K7-, OCH-, or vehicle-pulsed human CD1d-expressing T2 cells (T2-CD1d) or to K7-pulsed CD1d negative T2 cells (T2-) is shown. OCHHIGH clones consistently displayed greater proliferation than OCHLOW clones in response to OCH or vehicle pulsed T2-CD1d. cpm, counts per minute. Mean values ± s.e.m. are shown. (B) Cytokine secretion profiles of a representative pair of matched OCHHIGH and OCHLOW iNKT clones in response to the strong agonist ligand K7 and the partial agonist ligand OCH, presented by T2-CD1d, are shown. OCHHIGH iNKT clones exhibited much stronger cytokine secretion than OCHLOW iNKT cells in response to OCH-pulsed T2-CD1d, while cytokine secretion was similar for both in response to K7-pulsed T2-CD1d. (C) Autoreactive cytokine release in response to T2-CD1d in the absence of added exogenous ligands is shown for four matched pairs of OCHHIGH and OCHLOW iNKT clones. OCHHIGH but not OCHLOW iNKT clones consistently exhibited substantial autoreactive cytokine secretion. (D) Specific lysis of K7- (filled markers) and OCH- (unfilled markers) pulsed T2-CD1d targets is shown for three matched pairs of OCHHIGH and OCHLOW iNKT clones from different donors.