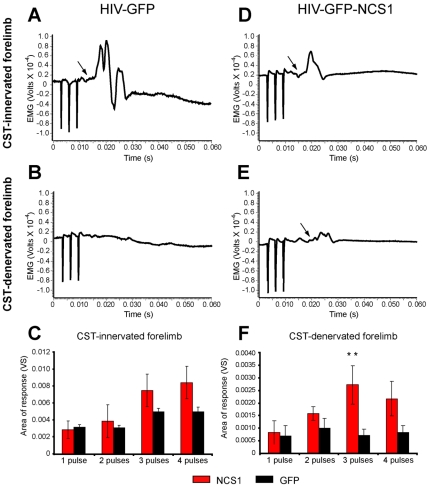
Figure 9. Electromyogram activity observed with NCS1-induced axon collateral sprouting.
(A–B) Typical example of electromyogram (EMG) recorded from the CST-innervated forelimb (A) and absent EMG from the CST-denervated forelimb (B) following surface stimulation of the contralateral sensorimotor cortex with 3 pulses (3 ms apart) in rats intracortically injected with control HIV-GFP lentivector. (D–E) In NCS1-transduced rats, an EMG from the CST-innervated forelimb and a delayed EMG from the CST-denervated forelimb following surface stimulation of the contralateral sensorimotor cortex was detected. (C) No significant difference was observed with the CST-innervated forelimb between groups. (F) However, the CST-denervated forelimb shows a significantly greater evoked response after 3 pulses following NCS1-transduced (red bar) compared to the control-transduced (black bar) rats. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM from n = 4 rats per group. ** p<0.01, two-way ANOVA, Tukey post hoc test.