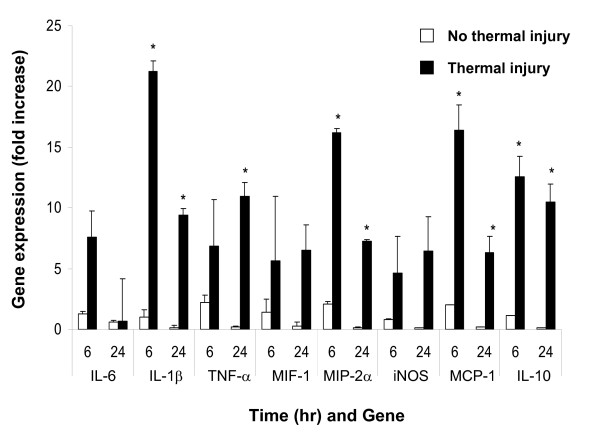
Figure 4.
Systemic inflammation in the lung following a local full-thickness cutaneous thermal injury. Lungs from MRL/MpJ mice with ear-hole wounds ± thermal injury were evaluated for inflammatory gene expression. Severe thermal trauma induced significant elevation of lung inflammatory chemokine, and iNOS transcript levels at 6 and 24 hr post injury in the lung. Gene levels were assessed using quantitative RT-PCR as described in the Material and Methods. The expression of transcripts normalized to 18 s in the lung at 6 and 24 hrs post thermal injury were determined. Each value represents the mean ± SEM fold increase in gene expression versus lung tissue from uninjured control MRL/MpJ mice (n = 5-7 mice/time point, * P < 0.05 as compared with baseline time 0-hr levels)