Figure 1.
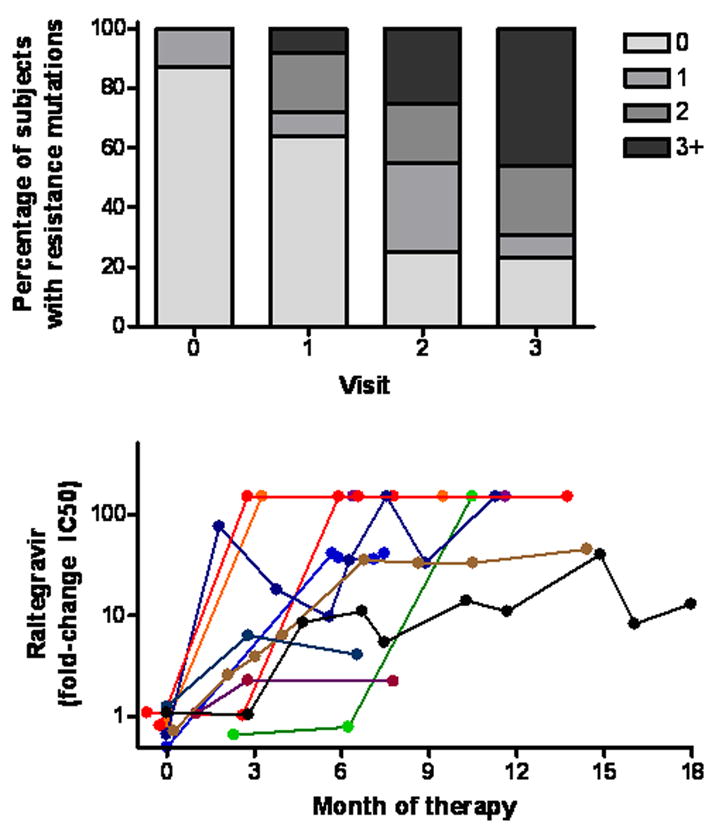
Incomplete viral suppression on an integrase inhibitor based regimen is associated with continued viral evolution, as defined by the number of primary and secondary integrase mutations present at each consecutive visit (Panel A) and by the level of phenotypic resistance (Panel B). All subjects who had incomplete viral suppression and who remained on an integrase inhibitor-based regimen and who had interpretable genotypic resistance data are shown in Panel A (n=23, 25, 20 and 13 at baseline and visits 1–3, respectfully). All subjects who eventually developed evidence of integrase resistance are shown in Panel B (n=11).
