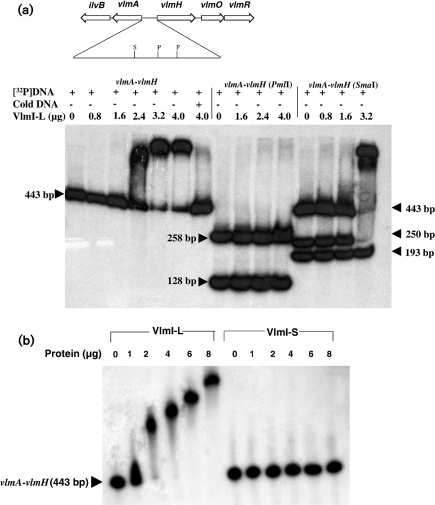
Fig. 5.
(a) DNA gel shift assays showing binding of VlmI-L to a 443 bp vlmA–vlmH intergenic DNA fragment. The 443 bp DNA fragment was labelled at both ends with [α-32P]dCTP. The assays in lanes 1–6 show the behaviour when the complete 443 bp fragment was mixed with increasing amounts of VlmI-L. Lane 7 shows the behaviour when the labelled DNA fragment plus 4 μg VlmI-L was mixed with a 50-fold excess of the unlabelled 443 bp DNA fragment. Lanes 8–11 show the results of gel shift assays after the labelled 443 bp fragment was digested with PmlI, and lanes 12–15 show the results of gel shift assays after digestion of the same fragment with SmaI. The quantity of VlmI used in each assay is shown at the top of each lane. S and P show the positions of the SmaI and PmlI sites, respectively. (b) Comparison of DNA gel shifts produced by VlmI-L and VlmI-S with a radiolabelled 443 bp vlmA–vlmH intergenic DNA fragment.