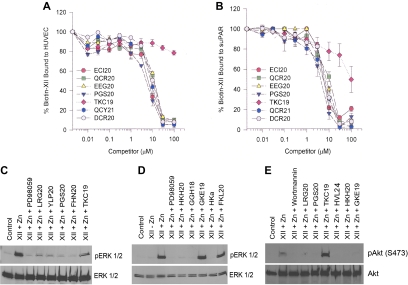
Figure 3.
Mapping FXII binding and signalling on uPAR. (A-B) Biotin-FXII binding to HUVECs or SuPAR. Biotin-FXII (20nM) in the presence of 50μM Zn2+ was incubated with cultured HUVEC monolayers (A) in microtiter plates in HEPES (N-2-hydroxyethylpiperazine-n′-2-ethanesulfonic acid) buffer as previously reported7 in the absence or presence of increasing concentrations of overlapping uPAR domain 2 peptides ECI20, QCR20, EEG20, PGS20, or TKC19 (see Table 1) or uPAR domain 3 peptides OCY21 or DCR20.8 Similar experiments were performed with microtiter plates coated with 1 μg/mL SuPAR in 0.1M Na2CO3, pH 9.6 buffer (B). (A-B) Means ± SDs of 3 or more competition inhibition binding experiments. (C-E) Mapping the regions on uPAR or high molecular weight kininogen that compete with FXII binding to HUVECs to prevent FXII stimulation of ERK1/2 or Akt phosphorylation. (C-D) The regions on uPAR or HK that influence FXII-induced ERK1/2 phosphorylation are examined. (E) The regions on both uPAR and HK that influence FXII-induced Akt phosphorylation are examined. In all panels “Control” represents serum-starved cells alone. (C-D) FXII (62nM) and 50μM Zn2+ were incubated with serum-starved HUVECs in the absence or presence of 50μM PD98059 or 300μM peptide LRG20, YLP20, PGS20, FHN20, or TKC19 from uPAR (C) or 300μM peptide HKH20, GGH18, GKE19, or FKL20 or HKa (D). (E) FXII (62nM) and 50μM Zn2+ were incubated with serum-starved HUVECs in the absence or presence of 30nM Wortmannin or 300μM peptide LRG20, PGS20, TKC19, HVL24, HKH20, or GKE19 (Table 1). This figure is 1 experiment under these conditions and with these peptides.