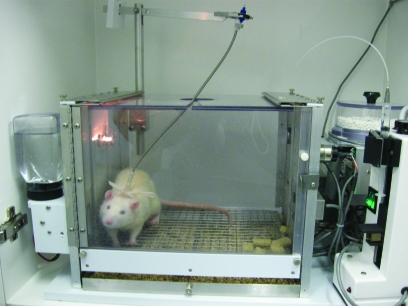
Figure 3.
An example of using the extended-access drug self-administration procedure to predict vulnerability, in this case sex differences in levels of cocaine intake. (Left) Male and female rats were compared in their responses for cocaine under extended access conditions by using a discrete trial procedure (4 trials/h, 1.5 mg/kg/infusion). Results show that female rats take more cocaine over a 10-d access period as compared with male rats. (Right) When responding is assessed 10 d after extended-access cocaine self-administration, female but not male rats show enhanced levels of progressive-ratio responding as compared with female and male rats tested after short-access cocaine self-administration (for example, maximum of 20 infusions/d for 5 d). n = 7 to 12. *Significant (P < 0.05) difference between male and female rats.